What Is the Difference Between a Proxy and a VPN?
VPNs and proxy servers both redirect your traffic through a remote server. However, each tool affects your privacy, security, and user experience in different ways.
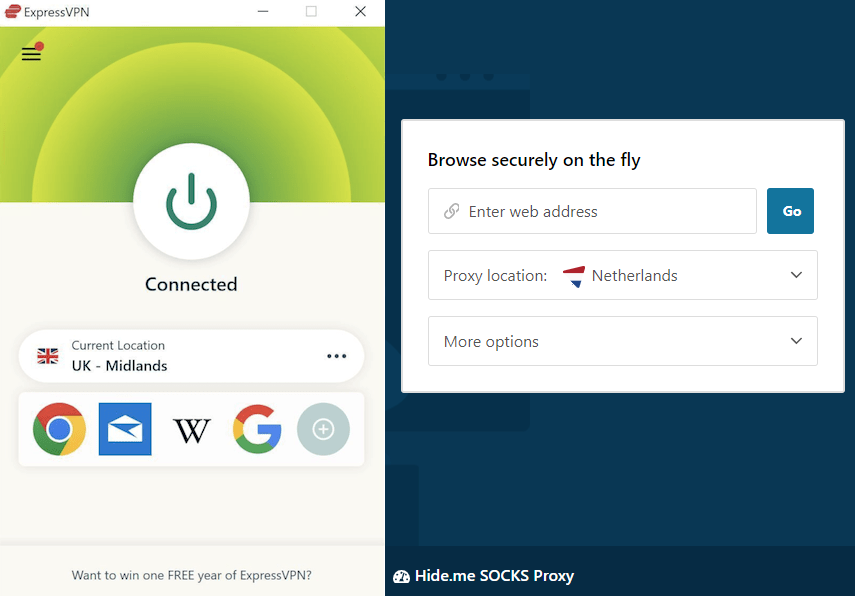
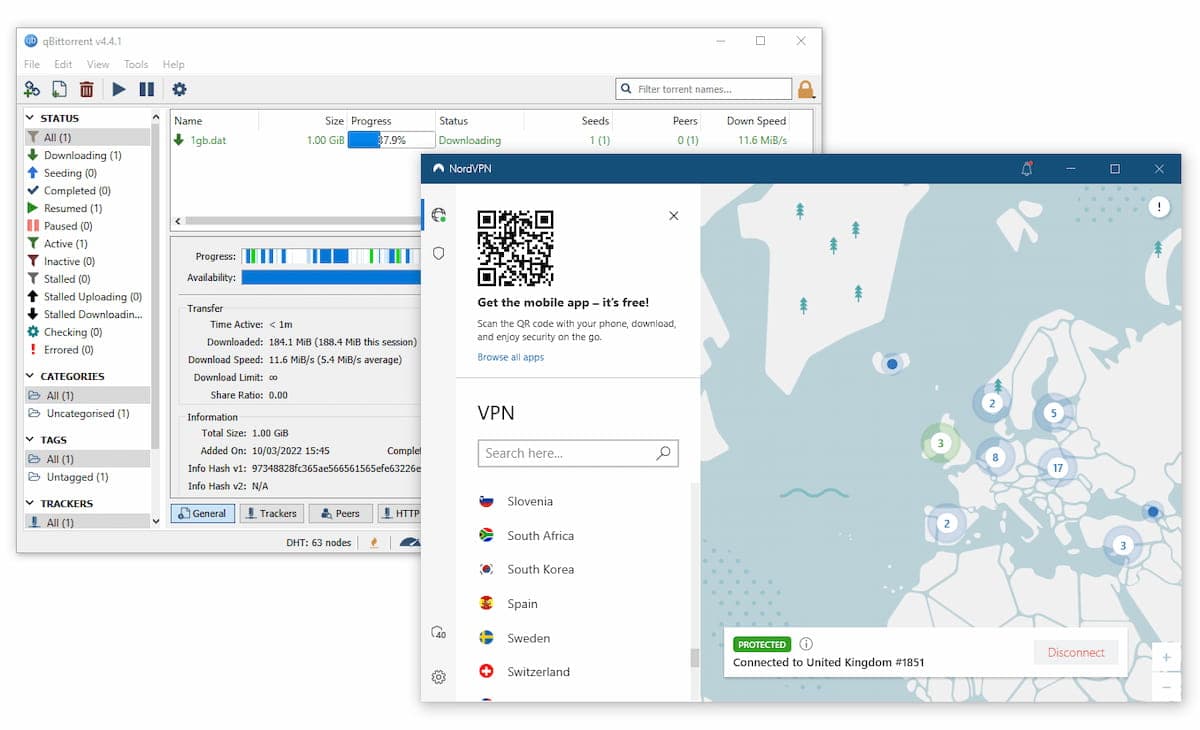
A VPN application (left) compared to a web proxy (right).
Here are the main differences between a proxy and a VPN:
Encryption
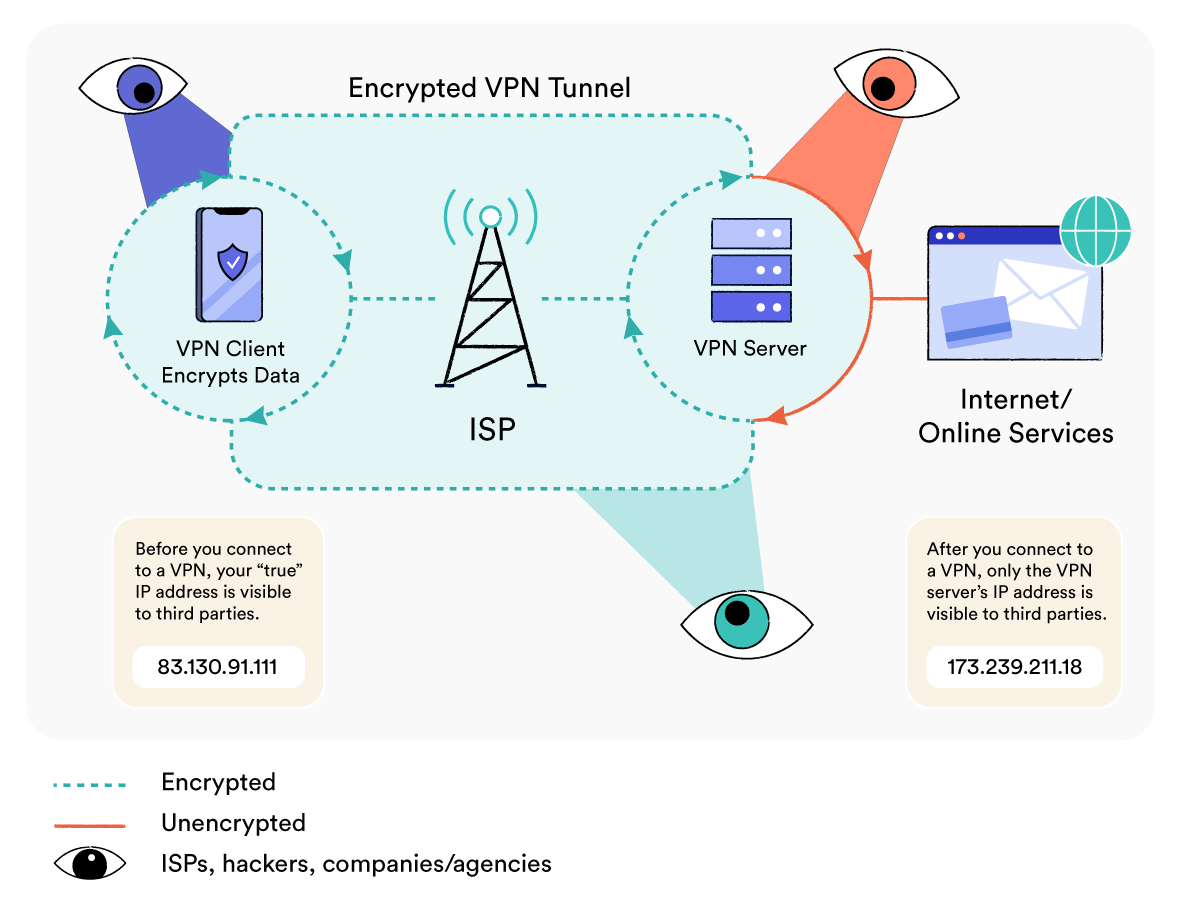
A VPN encrypts your traffic to protect you from ISP tracking, government surveillance, and spying on open networks.
If you’re using a good VPN, you’ll be able to choose your connection protocol and encryption strength — typically with the option of using WireGuard in combination with the AES-256 cipher.
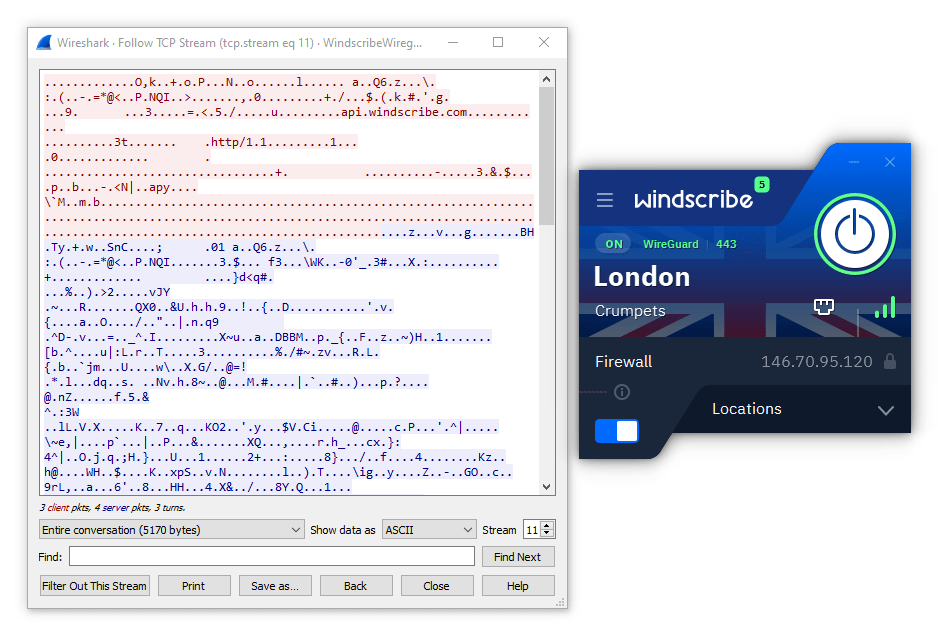
Using Wireshark, the unintelligible letters and numbers verify Windscribe’s connections are encrypted.
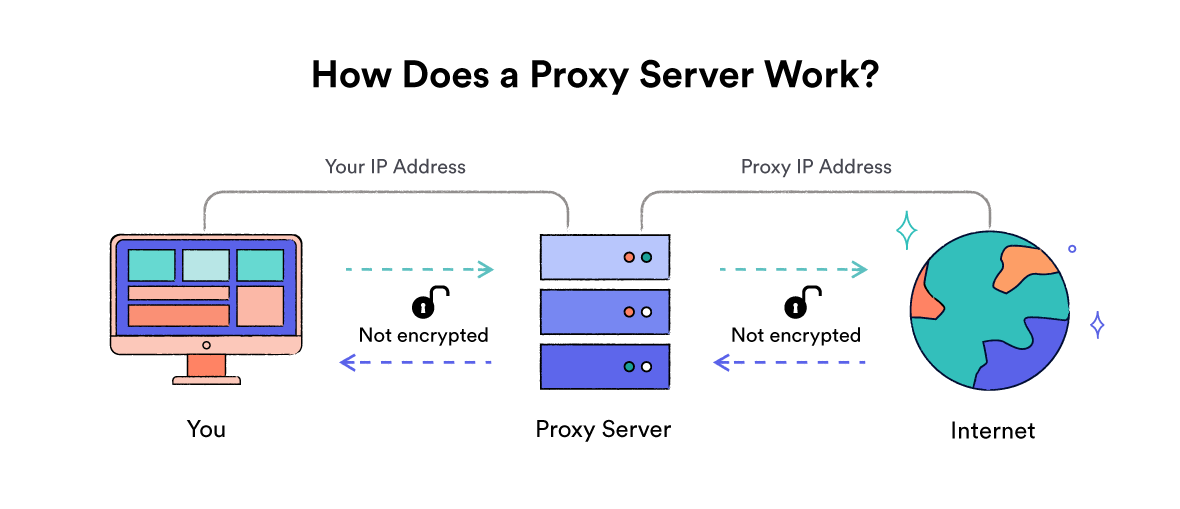
Most web proxies do not encrypt your traffic. If they do use some form of encryption, it’s typically the same protocol used to secure HTTPS websites, which is far weaker than the encryption you’d get using a secure VPN.
Coverage
VPN services typically come packaged in applications that are installed on your device. When you open the application and connect to a VPN server, the software reroutes and encrypts all of the internet traffic leaving your device.
Proxies can be set up in your operating system to work in a similar way. However, in the vast majority of cases, proxies are set up in just one application, like your web browser.
In this case, only the traffic from that window or application will go through the proxy server. If you send data from another application on your device – a torrenting client, for example – your true IP address will be visible to anyone spying on your activity.
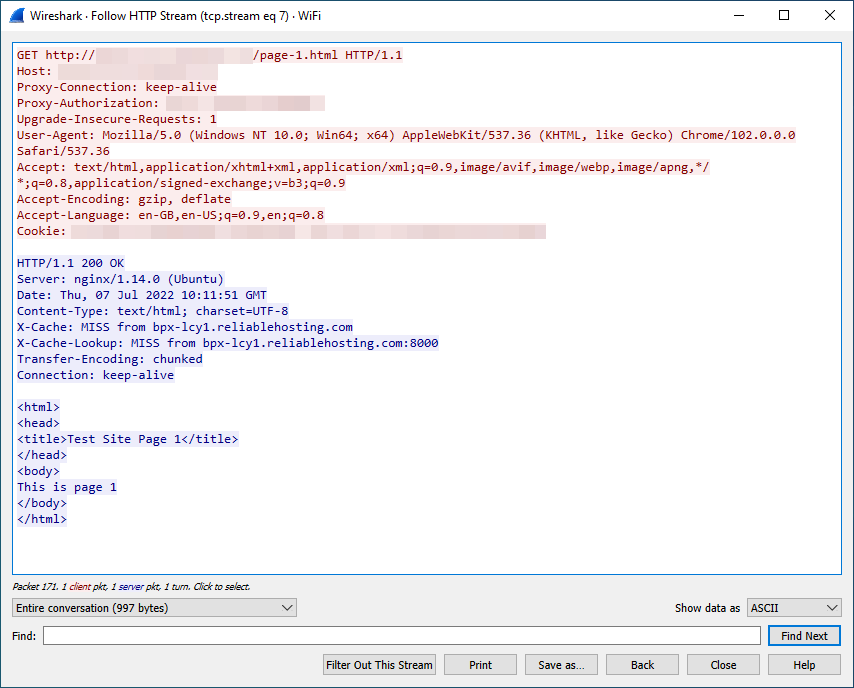
StrongVPN’s unencrypted proxy extension failed to conceal our traffic.
Price
It’s expensive to maintain a secure and reliable server network, so high-quality VPN services usually cost money. While safe free VPN services do exist, they usually come with data usage caps, slow speeds, and other limitations.
Web proxies are mostly free, and they’re often very limited as a result. They may have poor or non-existent customer support, lackluster security, slow speeds, and their servers can be highly-congested.
It’s possible to pay for a proxy server that will have better features, stronger security, and faster speeds, but free proxies are much more common.
Support
VPN services are usually run by companies with a financial incentive to provide the best service possible. For this reason, they are more reliable than proxies, and offer strong customer support. Proxies — especially free ones — are typically much smaller operations with no real support network.
VPN services usually offer reliable customer support.
Trustworthiness
In simple terms, it’s risky to use a free proxy. It’s not uncommon for free web proxies to harvest user data to sell to advertisers, and some have been known to inject malicious code into user traffic.
The same applies to many free VPN services: there are a handful of trustworthy free VPNs, but even some of the most popular applications pose a risk to your privacy and security. In fact, many free VPN applications are actually simple web proxies in disguise.
Fortunately, paid-for VPNs are usually much more reputable. The VPN industry is competitive, so providers work hard to build and protect their reputations. In the best cases, they’ll store no identifying information about your connection, and they’ll commission external audits to prove it.
Speed
Encrypting and rerouting your traffic with a VPN reduces your internet speed — though usually by a negligible amount. In our testing, the fastest VPN services reduced our internet speeds by less than 7% when connecting to a server in the same country.
Nevertheless, good proxies are often faster than VPN services. A proxy doesn’t use strong encryption or a tunneling protocol, both of which can slow down your connection somewhat.
In addition, a proxy can cache files. If you request a file another proxy user has already downloaded, the proxy can send it to you without waiting to download it again. This can make your web browsing feel faster.
Ease of Use
Using a web proxy is incredibly easy. You simply navigate to the proxy’s website in your browser and enter the URL of the website you’d like to visit.
Other types of proxy require some configuration to set up in your application or operating system.
A VPN requires some installation, but the application is easy to use once it’s installed. For most basic activities, you simply choose your preferred server from a list and then press one button to connect.