VPN Security Vulnerabilities Increased 47% in 2023
The number of reported VPN vulnerabilities increased by 47% in 2023 compared to the average over the two years prior, with a 43% increase in confidentiality impact and a 40% rise in severity. Cisco, Zyxel and SoftEther were the most affected vendors in 2023.
First published November 29, 2023. Last updated with the complete data for the remainder of 2023, and a projection for 2024.
- 314 VPN vulnerabilities have been disclosed since 2021
- 2023: 133 VPN vulnerabilities disclosed with an average base score of 7.35
- 2022: 93 VPN vulnerabilities disclosed, average base score of 7.52
- 2021: 88 VPN vulnerabilities disclosed, average base score of 7.46
- At least 20 vulnerabilities are known to have been exploited, according to CISA.
- Cisco, Zyxel and OpenVPN are the most affected vendors across the entire three year time period
- Products involved in the most severe vulnerabilities include: Synology VPN Plus Server, Zyxel ATP Firmware and Cisco Small Business Routers
- Most common attack types: Code Execution and Injection (68 vulnerabilities), Denial of Service (54 vulnerabilities), Privilege Escalation (39 vulnerabilities) and Information Disclosure and Data Leaks (35 vulnerabilities)
- The average Impact Score of VPN vulnerabilities is 4.7 out of 6
- The most common Attack Vector was Network based (64% of vulnerabilities)
- A further 26% increase in VPN Vulnerabilities is projected in 2024
VPN Vulnerabilities Since 2021
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become crucial tools for businesses and individuals alike. However, their role handling highly sensitive data also makes them prime targets for exploitation.
Using the American National Vulnerability Database (NVD) we investigated the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures system in order to examine the extent of the threats posed to VPNs. In particular we have focused on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which scores each vulnerability on a scale from 0 to 10 in order to represent the severity of an information security vulnerability.
The CVSS base score is composed of a variety of subscores, including the Impact Score, which is a scale of 0 to 6 representing multiple impact metrics, such as confidentiality impact, integrity impact, and the availability impact of a successfully exploited vulnerability.
Our comprehensive data set reveals a total of 314 VPN vulnerabilities disclosed since 2021. Among these, the most common are Code Execution and Injection, Denial of Service, Privilege Escalation, and Information Disclosure vulnerabilities.
VPN VULNERABILITIES IN 2024
We predict that there will be 163 VPN vulnerabilities in 2024, a further 22% increase on 2023. This projection is based on trends we have identified in the numbers of VPN vulnerabilities between 2021 and 2023. For more detailed predictions jump to the 2024 Projection section of this report.
The most affected vendors across the past three years have been Cisco, Zyxel, and OpenVPN.
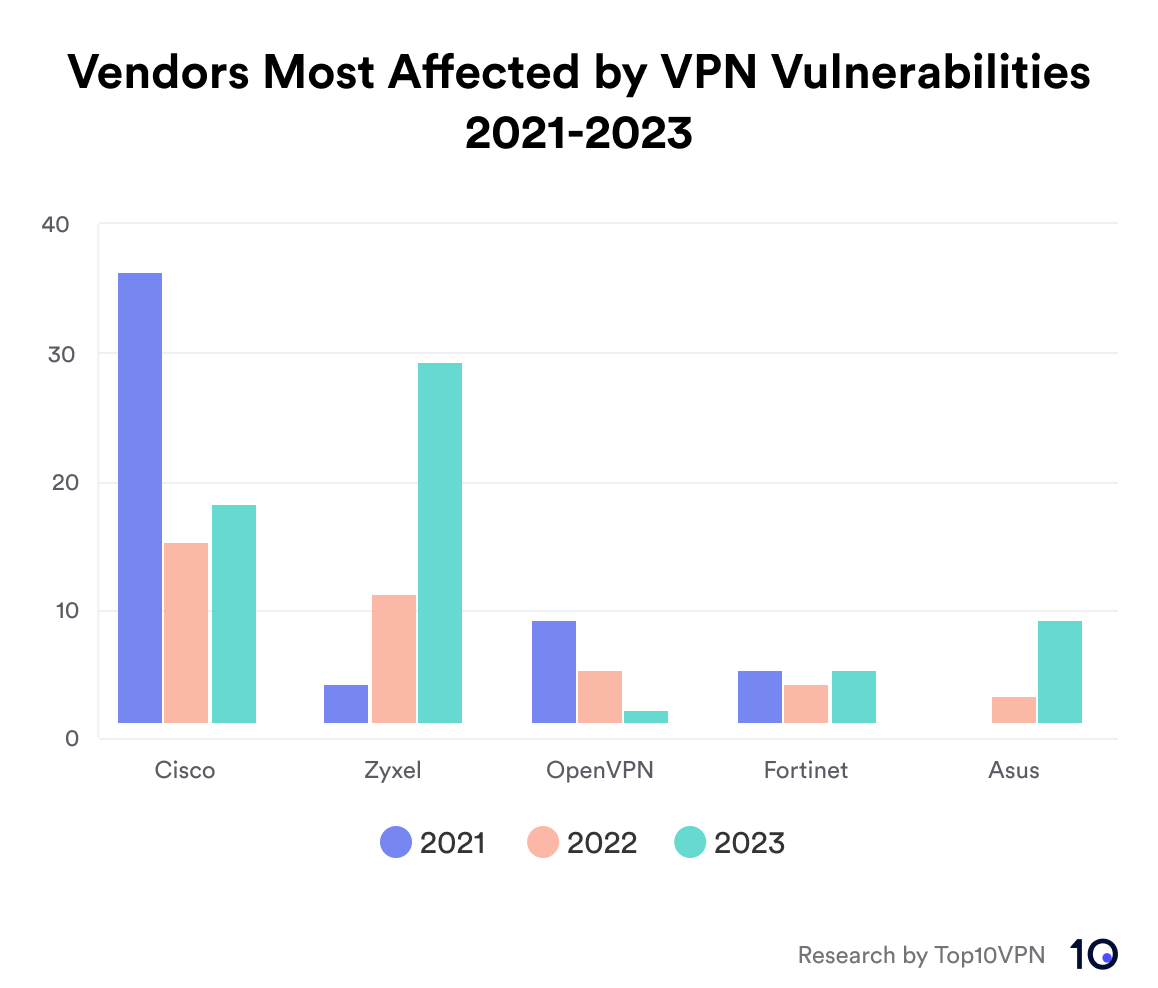
Chart showing vendors most affected by VPN vulnerabilities between 2021 and 2023
When comparing the total number of vulnerabilities affecting a vendor, it’s important to consider the breadth of that vendor’s product offering. The greater the range of VPN software, the greater the scope for vulnerabilities to occur.
Note also that most of the vulnerabilities disclosed in this research have now been patched and not all of them are thought to have been exploited.
The products affected by the vulnerabilities discussed throughout this research are primarily enterprise VPNs, rather than personal-use VPNs. In most cases the vulnerabilities impact businesses and corporations rather than individual users.
Our motivation for this research is to promote best practices among VPN providers and users. The findings underscore the importance of adhering to best practices in VPN security, such as regular updates, two-factor authentication (2FA), and vigilant monitoring to mitigate the risks posed by these vulnerabilities.
VPN Vulnerabilities 2021 - 2023
In 2023, the surge in vulnerabilities affecting VPNs, which increased by 43% compared to the previous year, represented a notable shift in the cybersecurity landscape.
This alarming trend emphasizes the vital need for robust cyber defenses as leading vendors such as Zyxel, Cisco, and SoftEtherVPN grapple with an escalating number of network-based vulnerabilities. The severity of these vulnerabilities was particularly concerning, with a high percentage threatening the confidentiality and integrity of systems.
For data on the full scope of VPN vulnerabilities disclosed since 2021, see the VPN Vulnerabilities 2021-2023 Data Sheet.
2023
- 133 vulnerabilities
- 7 known exploited vulnerabilities, according to CISA
- Most affected vendors: Zyxel, Cisco and SoftEtherVPN
- Attack Vector: 93 Network (70%), 29 Local (22%), 11 Adjacent Network (8%)
- Severity: 15 critical (11%), 75 High (57%), 43 Medium (32%)
- Average Base Score: 7.35
- Average Impact Score: 4.6
- Confidentiality Impact: 82 High (62%)
2023 was marked by a disconcerting increase in the number of vulnerabilities affecting VPN technologies. 133 VPN vulnerabilities were reported last year, which was 47% more than the average over the two years prior, highlighting an escalating challenge for cybersecurity professionals.
The most impacted vendors include Zyxel, a Taiwanese broadband provider, Cisco, an American-based digital communications technology corporation and SoftEtherVPN a free open-source VPN client and server software. Vendors which experienced the highest jumps in disclosed vulnerabilities included Juniper Networks, Stormshield and ASUS, with the figures being over 7 times higher than in the previous two year average.
Attack vectors were primarily network-based, accounting for 70% of the incidents. This attack vector accounted for 16% more of all vulnerabilities in 2023 than it did on average in 2021-22. Local and adjacent network vectors were the next most common in 2023. Almost six in ten (57%) of vulnerabilities were classified as high severity, while 11% were classified as critical. The average base score, calculated using the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), was 7.35.
Another notable area of concern was the confidentiality impact, a component of the CVSS base score, which refers to the disclosure of sensitive information to authorized and unauthorized users. Over one third (62%) of vulnerabilities were rated as having high confidentiality impact, which indicates that the attacker has full access to all resources in the impacted system, including sensitive information, a 41% increase from previous years based on year-to-date data.
The Most Critical VPN Vulnerabilities of 2023
Synology Remote Desktop Compromise: CVE-2022-43931
An out-of-bounds write vulnerability was discovered in the Remote Desktop functionality of Synology VPN Plus Server versions before 1.4.3-0534 and 1.4.4-0635. This flaw allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands through unspecified vectors, presenting a significant risk to affected systems. Being the only instance in our data set with a maximum base score of 10, this vulnerability stands out for its severity and emphasizes the urgency for updates and patches.
Zyxel Command Execution Flaw: CVE-2023-28771
Zyxel’s firmware exhibited a critical flaw due to improper error message handling, affecting several of its series including ZyWALL/USG, VPN, USG FLEX, and ATP. The vulnerability could permit unauthenticated attackers to remotely execute OS commands by sending specially crafted packets to the device.
Soon after the vulnerability was announced, news followed reporting cases of exploitation of the injection flaw. One of the activities confirmed to exploit this vulnerability was a Mirai-based botnet malware, launching attacks in late May 2023.
The critical nature of the situation was further emphasised by reports from the American Hospital Association of the vulnerability, suggesting its potential impact on network security in the healthcare setting.[1]
Cisco Unauthorized File Upload: CVE-2023-20073
Cisco’s RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P Dual WAN Gigabit VPN Routers were found to have a vulnerability in their web-based management interface. This flaw allows for the unauthenticated, remote uploading of arbitrary files due to insufficient authorization enforcement. This poses a significant threat, providing attackers with the capability to compromise the integrity of the affected device. The impact is compounded by its network attack vector, reinforcing the criticality of this vulnerability.
The vulnerability had an impact on a variety of businesses utilising Cisco routers, as well as once again on the healthcare industry with reports alerting of the vulnerability posted on the British National Health Service website.[2]
2022
- 93 vulnerabilities
- 9 known exploited vulnerabilities
- Most affected vendors: Cisco, Zyxel, Linux
- Attack Vector: 56 Network (60%), 31 Local (33%), 5 Adjacent Network (5%), 1 Physical (1%)
- Severity: 14 Critical (15%), 52 High (56%), 24 Medium (26%), 3 Low (3%)
- Average Base Score: 7.52
- Average Impact Score: 4.7
- Confidentiality Impact: 59 High (63%)
There were 93 reported VPN vulnerabilities in 2022, an increase of 6% compared to the previous year. Cisco and Zyxel were the most frequently-affected vendors that year, while there were also many instances of vulnerabilities found in the Linux Kernel. While the majority of the vulnerabilities had a network-based attack vector, a single vulnerability with a physical attack vector was also recorded, the only instance in the entire data set. Zyxel also experienced one of the highest jumps in VPN vulnerabilties in comparison to the year prior, with a 233% increase from the vulnerabilities disclosed in 2021.
The severity levels remained concerning, with 15% of vulnerabilities rated as being critical and over half classified as high. The average base score hovered around 7.52, a very slight increase from the year prior. Confidentiality impact also remained a concern, with 63% of vulnerabilities being classified as having a high confidentiality impact.
The Most Critical VPN Vulnerabilities of 2022
OpenVPN Authentication Bypass: CVE-2022-0547
A significant vulnerability within OpenVPN versions 2.1 to 2.4.12 and 2.5.6 allowed for authentication bypass when configured with multiple external authentication plugins which made use of deferred authentication replies. By exploiting this, an attacker could potentially gain access with partially correct credentials.
InHand Networks InRouter 900 RCE Vulnerability: CVE-2022-27270
In 2022 the InRouter 900 industrial 4G router by InHand Networks was found to have a critical remote code execution vulnerability in firmware versions before v1.0.0.r11700. This flaw stemmed from the ‘ipsec_secrets’ component and could be exploited through a specifically crafted packet. With a high base score of 9.8, it posed a serious threat, allowing attackers network-based code injection and execution capabilities.
Netgear Buffer Overflow Vulnerabilities: CVE-2022-44196 to CVE-2022-44199
Multiple buffer overflow vulnerabilities were identified in the OpenVPN server component of Netgear R7000P routers, affecting various firmware versions. These vulnerabilities could be exploited via specific parameters in the OpenVPN configuration, potentially leading to system compromise.
2021
- 88 vulnerabilities
- 4 known exploited vulnerabilities
- Most affected vendors: Cisco, OpenVPN, Citrix
- Attack Vector: 53 Network (60%), 32 Local (36%), 3 Adjacent Network (3%)
- Severity: 13 Critical (15%), 50 High (57%), 25 Medium (28%)
- Average Base Score: 7.46
- Average Impact Score: 4.67
- Confidentiality Impact: 56 High (64%)
There were 88 reported VPN vulnerabilities in 2021. Cisco was again one of the most affected vendors, alongside OpenVPN and Citrix, an American cloud computing company. As with the two years that followed, the vulnerabilities were predominantly network-based, however over a third of vulnerabilities also occurred via local attack vectors.
Critical vulnerabilities constituted 15% of the total in 2021, while a high confidentiality impact was also observed in 64% of all VPN vulnerabilities in 2021. The average base score for all VPN vulnerabilities in 2021 was 7.46. This was the lowest score over the three years we analyzed, however it is still considered to be of high severity.
The Most Critical VPN Vulnerabilities of 2021
Cisco Routers Remote Code Execution: CVE-2021-1289 to 1295
Cisco Small Business RV Series Routers faced multiple vulnerabilities within their web-based management interface. These flaws could enable an unauthenticated, remote attacker to execute arbitrary code with root privileges on affected devices, simply by sending a malformed HTTP request.
Cisco Routers Command Injection: CVE-2021-1602
Another severe vulnerability was identified in the same Cisco Small Business RV Series Routers. Due to insufficient validation of user input in the web-based management interface, an unauthenticated attacker could execute arbitrary commands on the device’s operating system with root access.
Zyxel Firmware Authentication Bypass: CVE-2021-35029
Zyxel’s firmware for its USG/Zywall and other series was found to have an authentication bypass vulnerability, allowing a remote attacker to execute arbitrary commands. This was possible in firmware versions ranging from 4.35 to 5.01, again highlighting the need for stringent authentication protocols.
VPN Vulnerabilities By Type
The following table shows the number of VPN vulnerabilities reported in each identified category each year. Note that some vulnerabilities have been assigned to more than one category, which means that the sum total across all years and categories in the table (360) is higher than the total number of reported VPN vulnerabilities (314).
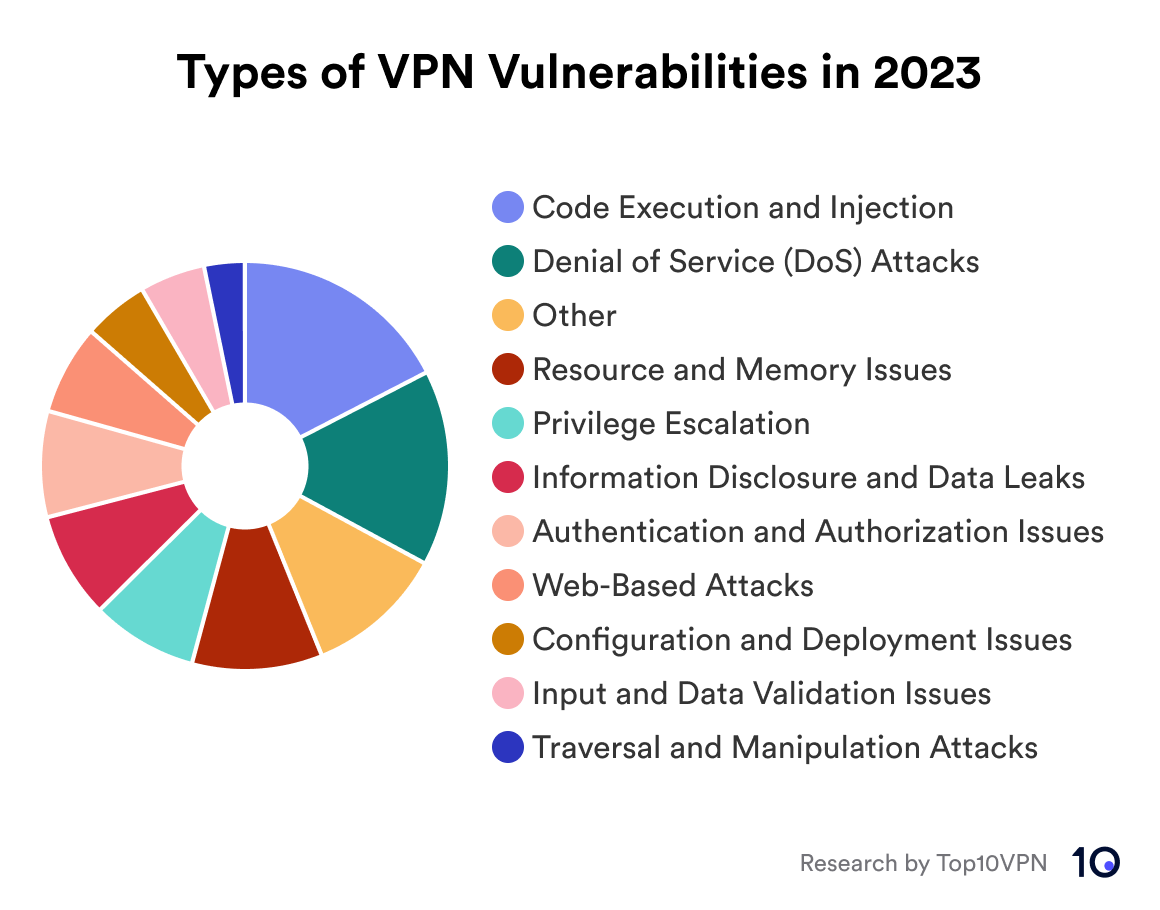
Pie chart showing the types of VPN vulnerabilities in 2023
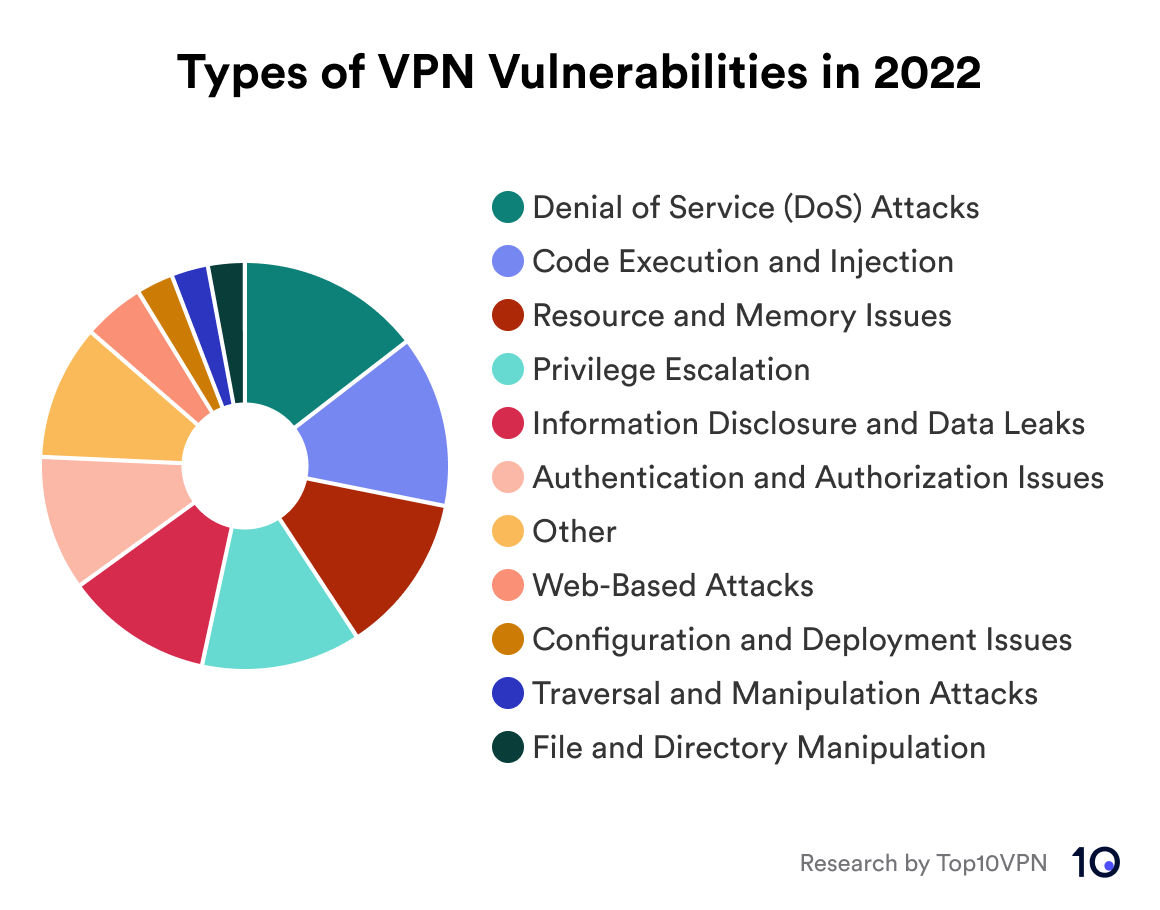
Pie chart showing the types of VPN vulnerabilities in 2022
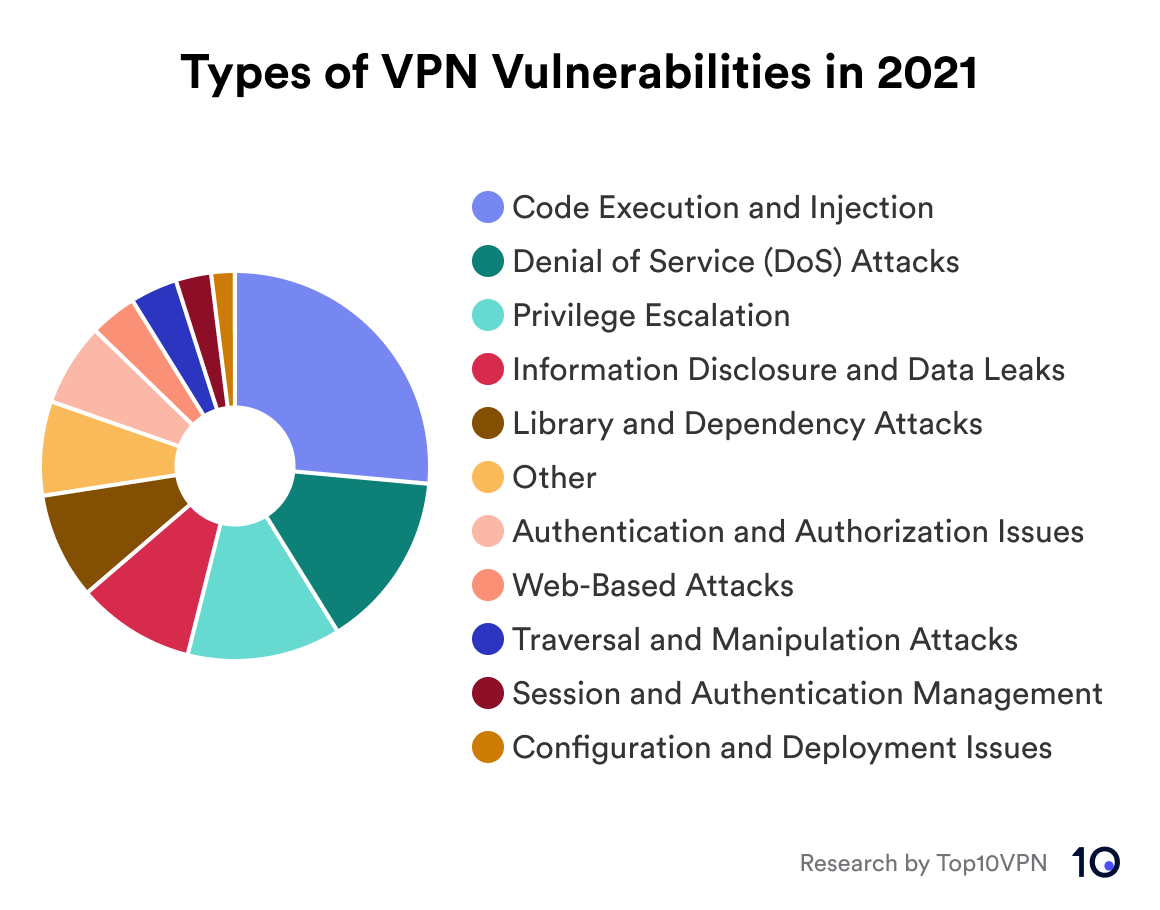
Pie chart showing the types of VPN vulnerabilities in 2021
Code Execution and Injection Vulnerabilities
Code Execution and Injection, which is the most common category of vulnerabilities across the dataset, refers to flaws and weaknesses in software that permit attackers to run malicious or arbitrary code. This can be done either within the context of an application or within the broader scope of an underlying operating system.
Over a fifth (21%) of VPN vulnerabilities between 2021 and 2023 could be categorized as code execution and injection, making it the most common vulnerability during that period, as well as specifically in 2021 and 2023. There was a 93% year-over-year spike in this kind of vulnerability in 2023 and a 32% increase compared to the average over the previous two years.
Some of the methods utilised in vulnerabilities present in this category include Dynamic Link Libraries (DLL) Hijacking and Injection, Command Injection and SQL injection.
DLL Hijacking involves exploiting the way some applications search and load DLLs. If an attacker can trick an application into loading a malicious DLL, they can execute arbitrary code with the same privileges as the application. Command Injection involves attackers exploiting inadequate input validation mechanisms to insert or “inject” commands that the system will execute. Finally during SQL Injection malicious SQL statements are inserted into an entry field, leading to unauthorized database actions.
Many vulnerabilities stem from web interfaces used for device management, especially in VPN routers and other networking equipment, and a lack of, or inadequate, input validation. In addition to this, improper handling or validation of HTTP requests can allow for command or code injection. Execution of arbitrary code can lead to a wide range of malicious outcomes, from data breaches to device control. Some vulnerabilities can also lead to Denial of Service (DoS) conditions, where a device or service becomes unavailable.
Mitigation strategies against code execution and injection vulnerabilities include secure coding practices, rigorous input validation, regular vulnerability assessments by product vendors, as well as prompt application of software updates by the user. These practices are crucial to protect systems from being compromised by attackers exploiting such vulnerabilities.
There were 20 different vendors affected by vulnerabilities categorized as Code Execution and Injection, some of the most notable being Cisco, Zyxel and Synology. Synology was involved in the previously mentioned sole instance over the entire period with a maximum CVSS base score of 10.
Some examples of the most critical vulnerabilities in this category, all with a base score of 9.8 out of 10, include:
Zyxel Command Injection Flaw: CVE-2022-30525
In 2022, various Zyxel devices, ranging from the USG FLEX series to the VPN series, were identified with a critical OS command injection vulnerability. Specifically, firmware versions from 5.00 up to 5.21 Patch 1 were affected, allowing attackers to manipulate certain files and execute operating system commands on the compromised device.
This is another example of a Zyxel vulnerability which saw attempts of exploitation soon after its announcement. The severity of this vulnerability once again put the NHS at risk, with alerts of the affected platforms posted on the official website.[3]
Array Networks Remote Code Execution: CVE-2023-28461
In 2023 a severe remote code execution vulnerability impacted the Array AG Series and vxAG solutions (up to version 9.4.0.481) from Array Networks. Unauthorized users could exploit this flaw by using a ‘flags’ attribute in an HTTP header to browse the filesystem of the SSL VPN gateway, leading to potential system compromise. In a statement in March, Array Networks advised a fix was imminent, which was made available later that month. [4]
Milesight VPN Authentication Bypass: CVE-2023-22319
Milesight’s VPN software version 2.0.2 was found to have a SQL injection vulnerability within its LoginAuth function in 2023, allowing for an authentication bypass through a specially crafted network request. This vulnerability could enable attackers to send malicious packets to exploit the system.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
The ‘Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks’ category of vulnerabilities concerns situations where attackers aim to interrupt or suspend the services of a host connected to the internet. This typically involves overwhelming a system with a flood of internet traffic, although other methods can be used. The result is that legitimate users are unable to access the system or its services.
There were 54 instances of DoS based vulnerabilities affecting VPNs between 2021 and 2023. It was the most common type of VPN vulnerability in 2022. Nevertheless, there was a 60% increase in this type of vulnerability recorded in 2023 than there was on average over the previous two years, the highest increase across the top five categories.
Methods seen in vulnerabilities throughout this category include using specially designed packets or requests that the system cannot handle appropriately, overloading system resources, such as memory, which can render a system unresponsive, or inputting incorrect or unexpected data values causing crashes or unanticipated behaviors. Vulnerabilities in this category stem from issues of prioritizing and managing network traffic, a lack of proper input validation and inaccurate or incomplete handling of specific network protocols.
Mitigation strategies to safeguard against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks involve implementing a network architecture which can distribute traffic evenly and prevent system overload, employing rate limiting, and configuring firewalls and routers to reject any suspicious requests.
There were 14 different vendors affected by this type of vulnerability, including Cisco, OpenVPN and SoftEther VPN. The average CVSS base score of this category was 7.2, classifying it as being of a high severity.
Some of the most severe vulnerabilities in this category include:
Cisco Small Business Router Vulnerabilities: CVE-2021-1610
In 2021, Cisco’s Small Business RV Series routers were found to be susceptible to multiple severe vulnerabilities, enabling attackers to execute arbitrary code, cause a denial of service (DoS), or execute arbitrary commands. Specifically, the RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P models were affected. The vulnerabilities had a base score of 9.8 out of 10, indicating a significant risk over the network, with potential serious consequences for confidentiality.
Cisco NX-OS Software DoS Issue: CVE-2021-1587
Another 2021 vulnerability in Cisco’s repertoire, rated with a base score of 8.6, was discovered in the NX-OS Software, affecting devices part of a VXLAN EVPN fabric with the NGOAM feature enabled. This issue, due to the mishandling of specific packets, could allow an unauthenticated attacker to trigger high CPU usage and system resource depletion, leading to control plane instability and potential device restarts.
Moby Project Packet Injection Flaw: CVE-2023-28840
In 2023, a notable vulnerability was identified within the Moby Project, specifically within its Docker component. A weakness was found in the iptables rules setup for encrypted overlay networks, which could permit denial of service attacks or arbitrary data injection. This flaw had broad implications for Docker and its downstream products, prompting releases of patched versions to address the security gap. This vulnerability scored an 8.7 base score, marking it as a high-risk concern for networked environments.
Privilege Escalation Vulnerabilities
Privilege escalation vulnerabilities, which were the third most common category over the period, allow a user to gain elevated access to resources that are normally protected from an application or user. This could enable the attacker to take control of the affected system.
There were 39 instances of vulnerabilities in this category affecting VPNs during the last three years, the majority of which occurred in 2022 and 2021. This was the only category in the top five which did not experience an increase in 2023 compared to the two years prior.
Some of the common vulnerabilities in this category include exploitation of unquoted service paths, placing malicious files in directories, exploiting the loading of Dynamic Link Libraries (DLLs) to run arbitrary code, and exploiting weak or misconfigured permissions.
Many vulnerabilities are linked to services or daemons that run with high privileges. Some other points of exploitation include installers and configuration files which may contain insecure default settings or paths, or vulnerabilities within VPN settings, which could provide attackers significant system access.
This type of vulnerability affected 21 vendors, including Cisco and Zyxel, along with cybersecurity company Fortinet. The category had a base score of 7.7 making it the second more severe category out of the top five categories discussed in this research.
Proper user management, avoiding over-permissive settings, and following best practices in software design and system administration are crucial defenses against privilege escalation threats.
Examples of the most severe vulnerabilities in this category, all identified in 2022, include:
Netgear SQL Injection Flaw: CVE-2022-29383
A SQL injection vulnerability was found in the NETGEAR ProSafe SSL VPN firmware for models FVS336Gv2 and FVS336Gv3, where the USERDBDomains.Domainname parameter in cgi-bin/platform.cgi was improperly handled. This flaw could lead to privilege escalation and had a high severity with a base score of 9.8.
Android VPN Credential Leak: CVE-2022-20145
A vulnerability within Android’s Vpn.java file for Android-11 was disclosed, where a protocol downgrade attack could allow attackers to retrieve VPN credentials remotely. This could result in an escalation of privilege without the need for user interaction or additional execution privileges, especially when connected to a malicious Wi-Fi AP. The issue was critical, with a network attack vector and a base score of 9.8.
Fortinet FortiClient Privilege Escalation: CVE-2021-44169
Fortinet’s FortiClient for Windows (versions 6.0.10 and below, 6.2.9 and below, 6.4.7 and below, 7.0.3 and below) exhibited a vulnerability due to improper initialization, which could allow an attacker to gain administrative privileges by placing a malicious executable in the installer’s directory. This logic flaw had an 8.8 base score, which, while lower than the previous two examples, was combined with a maximum confidentiality score of 6.
Information Disclosure and Data Leaks
Information Disclosure and Data Leaks, which is the fourth most common type of VPN vulnerability we found, includes vulnerabilities where unauthorized individuals can access or retrieve sensitive or proprietary information that should be restricted. Such unauthorized access can lead to a breach of privacy, a compromise of system integrity, and even potential misuse of the disclosed information.
There were 35 instances of Information Disclosure and Data Leaks vulnerabilities affecting VPNs between 2021 and 2023. Reports of this type of vulnerability increased by 30% in 2023 compared to 2021 and 18% against the two-year average.
There were 24 different vendors affected by this type of vulnerability, the highest number affected by a single category. Affected vendors included Fortinet, McAfee and SoftEther VPN.
Some common types of vulnerabilities in this category include unauthorized users accessing or reading files they shouldn’t be able to, often due to misconfigurations or design flaws, sending data over the network without proper encryption, which can lead to information interception, and systems not sufficiently encrypting or masking sensitive data, making it easily accessible.
Information Disclosure and Data Leaks vulnerabilities can occur due to a variety of reasons, such as leaked session IDs or tokens, which can allow unauthorized users to hijack sessions, configuration files, which have not been properly secured, containing sensitive details and systems that don’t adequately sanitize logs or histories, which can inadvertently store sensitive data.
To prevent information disclosure and data leaks, it’s essential to enforce strict access control, utilize strong encryption, and maintain rigorous data handling protocols. Ensuring users have only necessary data access, encrypting stored and transmitted data, securing system configurations, and sanitizing logs can significantly reduce leak risks. Regular audits and timely patching of vulnerabilities are also crucial to safeguard sensitive information.
The average base score for this category was 6.6, which is the lowest average base score out of the top five most prevalent categories, being only classified as having Medium Severity on the CVSS scale. Nevertheless, the potential consequences of data leaks, particularly in today’s data-driven world, are a significant concern and addressing these vulnerabilities is paramount for businesses and individuals alike.
The most significant vulnerabilities in this category, all with a base score of 9.8 out of 10 include:
Snapdragon Certificate Validation Flaw: CVE-2020-11176
In 2021, a memory corruption vulnerability was discovered in the IPSec server across multiple Snapdragon platforms, including Auto, Compute, and various IoT devices. Specifically, the flaw arose from improper heap allocation during the processing of server certificates, which could lead to memory corruption.
OpenVPN Netfilter Flaw: CVE-2021-3773
A serious vulnerability in OpenVPN’s Netfilter, identified in 2021, allowed network-connected attackers to infer connection endpoint information, potentially paving the way for further traditional network attacks.
Ruijie Networks Remote Code Execution: CVE-2023-34644
In 2023, Ruijie Networks’ RG-EW series, among other devices, was found to have a remote code execution vulnerability. Attackers could exploit this by sending a crafted POST request to achieve the highest privileges.
Authentication and Authorization Issues
Authentication and authorization vulnerabilities, the fifth most common category of VPN vulnerabilities seen over the past three years, arise when there are defects or weaknesses in the process of verifying the identity of a user or granting the appropriate permissions to a user.
There have been 31 instances of authentication and authorization VPN vulnerabilities since 2021. While there was only a 18% year-on-year increase in 2023, there was a 86% increase compared to 2021. The 44% increase in this kind of VPN vulnerability in 2023 compared to the average over the previous two years is the second biggest among the top five most common categories in this report.
Common vulnerabilities found within this category include weaknesses in external software or plugins that allow access with partially correct or no credentials, crafted network requests, that allow unauthorized actions by sending manipulated network requests, misconfigured services bound to wrong configurations, exposing them to external threats, as well as Man-in-the-Middle attacks, where attackers intercept and manipulate communication between parties, leading to unauthorized access or data interception.
Points of exploitation related to this category include API endpoints, where attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in the application programming interfaces, servers with specific configurations that might be more vulnerable, and web interfaces like VPN portals or web servers that may be more exposed to these types of vulnerabilities.
Implementing multi-layered security, timely patching, and avoiding hardcoded or weak credentials are fundamental to mitigating the risks associated with these issues.
There were 12 vendors affected by this type of vulnerability, including SoftEther VPN, OpenVPN and Stormshield. The category had an average base score of 7.2, classifying it as having a High severity.
Some of the most significant vulnerabilities in this category, all with a base score of 9.8 out of 10 include:
Milesight VPN Authentication Flaw: CVE-2023-22844
The Milesight VPN version 2.0.2 was found to have an authentication bypass vulnerability within its verifyToken function, as reported in 2023. Attackers could exploit this by sending a specially-crafted network request, potentially granting unauthorized access.
Cisco Small Business VPN Bypass Issue: CVE-2022-20923
In 2022 Cisco’s Small Business RV Series routers were discovered to have a significant flaw in their IPSec VPN Server authentication process, allowing attackers to bypass authentication controls remotely. The vulnerability stemmed from improper password validation algorithm implementation.
Following the publication of this vulnerability, Cisco announced the authentication bypass flaw would not be patched as the affected devices have reached end-of-life. The company instead advised affected users to migrate to Cisco Small Business RV132W, RV160, or RV160W Routers.
Zyxel Firewall Authentication Bypass: CVE-2022-0342
Also in 2022, a broad range of Zyxel devices was susceptible to an authentication bypass in their firmware, affecting models from the USG/ZyWALL, USG FLEX, ATP, VPN, and NSG series. The flaw allowed attackers to circumvent web authentication and gain administrative device access.
VPN Vulnerabilities in 2024
The following is our projection of how VPN technologies will be affected by vulnerabilities in 2024. We used our 2021-2023 dataset as the basis for our model.
- 163 vulnerabilities projected in 2024
- Attack Vector: 123 Network (76%)
- Severity: 106 either High or Critical (65%)
- Average Base Score: 7.3
- Average Impact Score: 4.55
- Confidentiality Impact: 90 High (55%)
We predict that the number of vulnerabilities will once again increase in 2024. Based on the rate of increase in the number of vulnerabilities over the past three years, we estimate a 22% year-over-year increase to 163 reported VPN vulnerabilities in 2024. While this may not be as steep of an increase as experienced in 2023, it still means that in 2024 we expect to see the highest number of VPN based vulnerabilities to date.
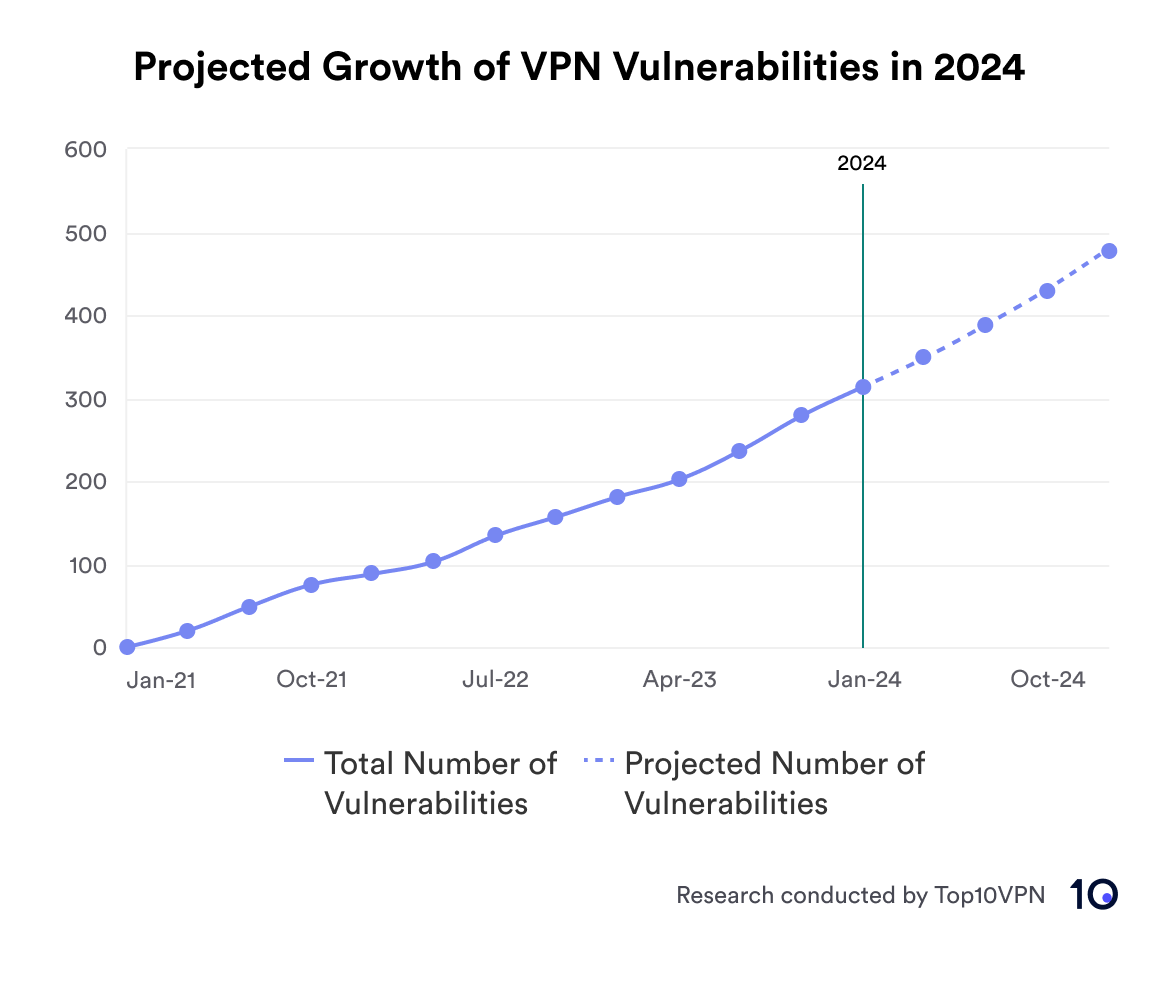
Chart showing the projected growth in the total number of VPN vulnerabilities in 2024
According to our projections, many of the most important metrics of these vulnerabilities should remain relatively stable over the upcoming year. Trends over the past three years suggest that average base and impact scores will decline slightly, as will the proportion of vulnerabilities with either high and critical severities, or a high confidentiality impact. However given the projected increase in the total number of VPN related vulnerabilities, the actual number of vulnerabilities with high severities and confidentiality impacts will likely be higher than in previous years.
We expect that the emerging trends in the types of VPN vulnerabilities identified over the past three years will also continue into 2024. In 2021 the five most common categories of vulnerabilities accounted for 68% of VPN vulnerabilities found but by 2023 that proportion dropped to 53%, or a 22% decline over that period. We expect that the nature of VPN vulnerabilities will continue this trend of becoming more diverse in the coming year.
In terms of types of VPN vulnerability, “Resource and Memory Issues”, “Input and Data Validation Issues” and “Middle-Man Attacks” were the categories with the biggest increases between 2021-23. Increases in the number of reported VPN vulnerabilities falling under these categories ranged from 200% to 600% or more. We expect to see further increases in these categories in 2024, in particular Middle-Man Attacks, which surged significantly in 2023.
2024 is already off to an alarming start, as less than two weeks into the year an authentication bypass vulnerability and a command injection vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-46805 and CVE-2024-21887, were found in the Ivanti Connect Secure software [5]. The vulnerabilities had respective base scores of 8.2 and 9.1, and the U.S. software company had confirmed that they had been exploited by hackers. With patches not expected to be available until the end of January 2024, this news sets a concerning precedent for the upcoming year in VPN vulnerabilities.
Methodology
In order to examine the scope of VPN vulnerabilities we used the United States National Vulnerability Database in order to collect all reported vulnerabilities between January 1st 2021 and November 28th 2023 related to VPNs, with additional data for the remainder of 2023 was collected in early January 2024. The data was then manually analyzed in order to identify the vendors and products involved as well as to categorize the vulnerabilities into specific categories.
For our 2024 prediction, we examined quarterly rates of change in the number of vulnerabilities identified between 2021 and 2023, and adjusted the projected figures according to the identified patterns.
The authors of all our investigations abide by the journalists’ code of conduct.
References
[1] https://www.aha.org/h-isac-white-reports/2023-05-01-h-isa-tlp-white-vulnerablilty-bulletin-critical-zyxel-vulnerability-cve-2023-28771 ↩
[2] https://digital.nhs.uk/cyber-alerts/2023/cc-4255 ↩
[3] https://digital.nhs.uk/cyber-alerts/2022/cc-4091 ↩
[4] https://support.arraynetworks.net/prx/001/http/supportportal.arraynetworks.net/documentation/FieldNotice/Array_Networks_Security_Advisory_for_Remote_Code_Execution_Vulnerability_AG.pdf ↩
[5] https://techcrunch.com/2024/01/11/ivanti-connect-vpn-zero-days-china-backed-hackers/↩