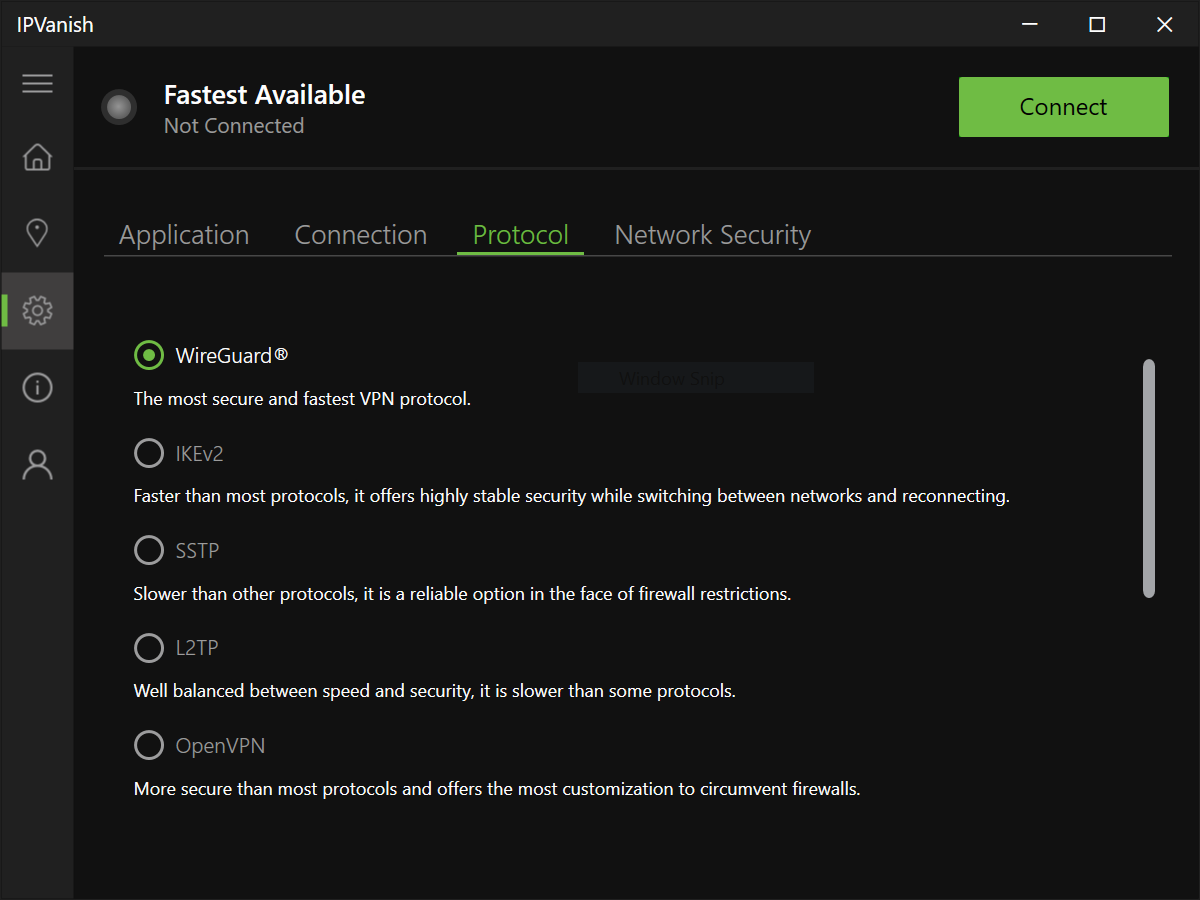
VPN services are designed to be simple. That’s great when they’re working properly, but frustrating when they’re not.
Often, VPN apps don’t explain why the VPN won’t connect. Instead, you’ll see the connection icon spin indefinitely, or the app will simply say “unable to connect”.
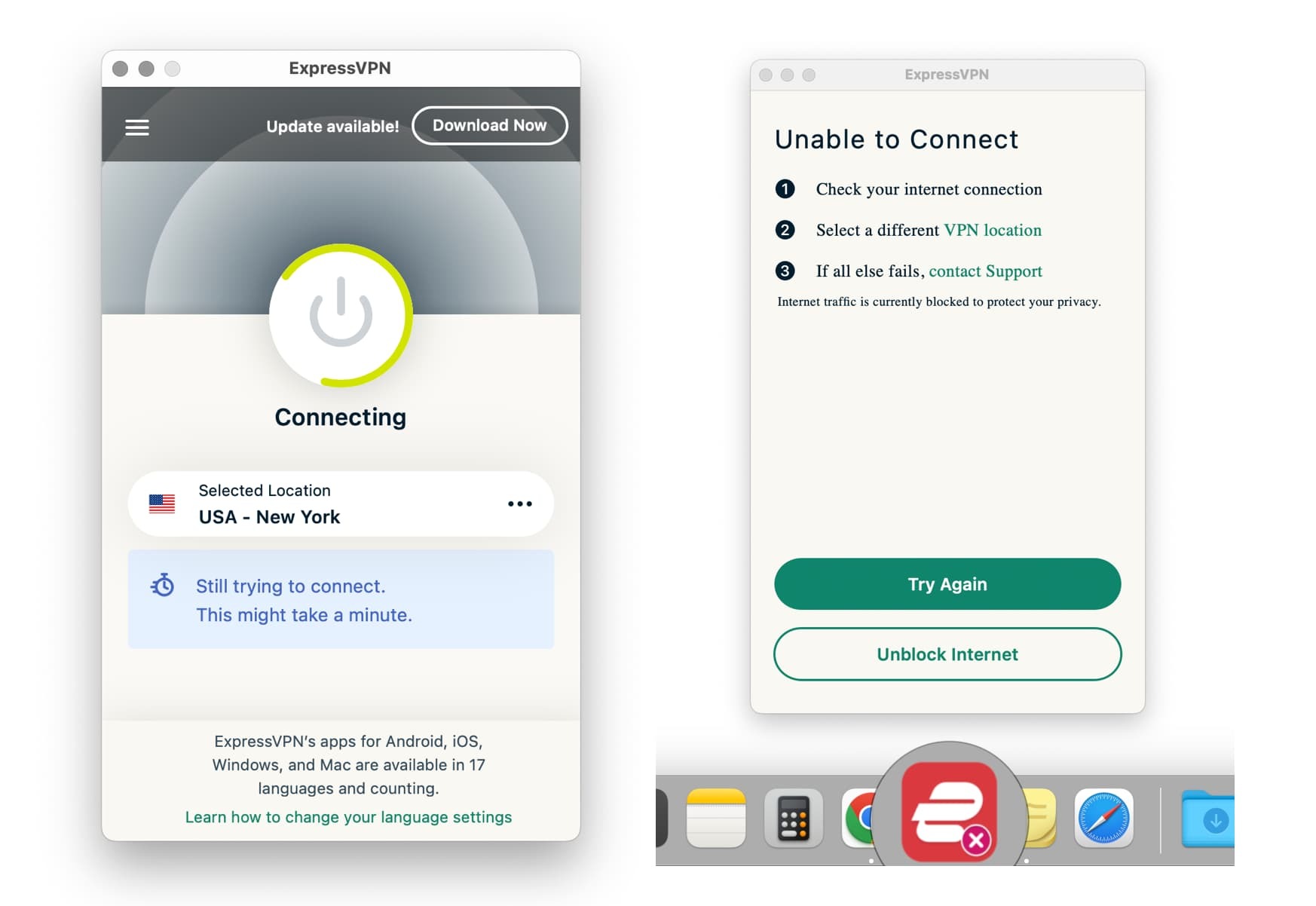
ExpressVPN failing to connect.
Here’s a list of common reasons why your VPN won’t connect to a server:
1. Your Internet Connection is Unstable
A VPN relies on a stable internet connection to function correctly. If your network is experiencing disruptions or your internet service provider (ISP) has issues, it can prevent your VPN from connecting.
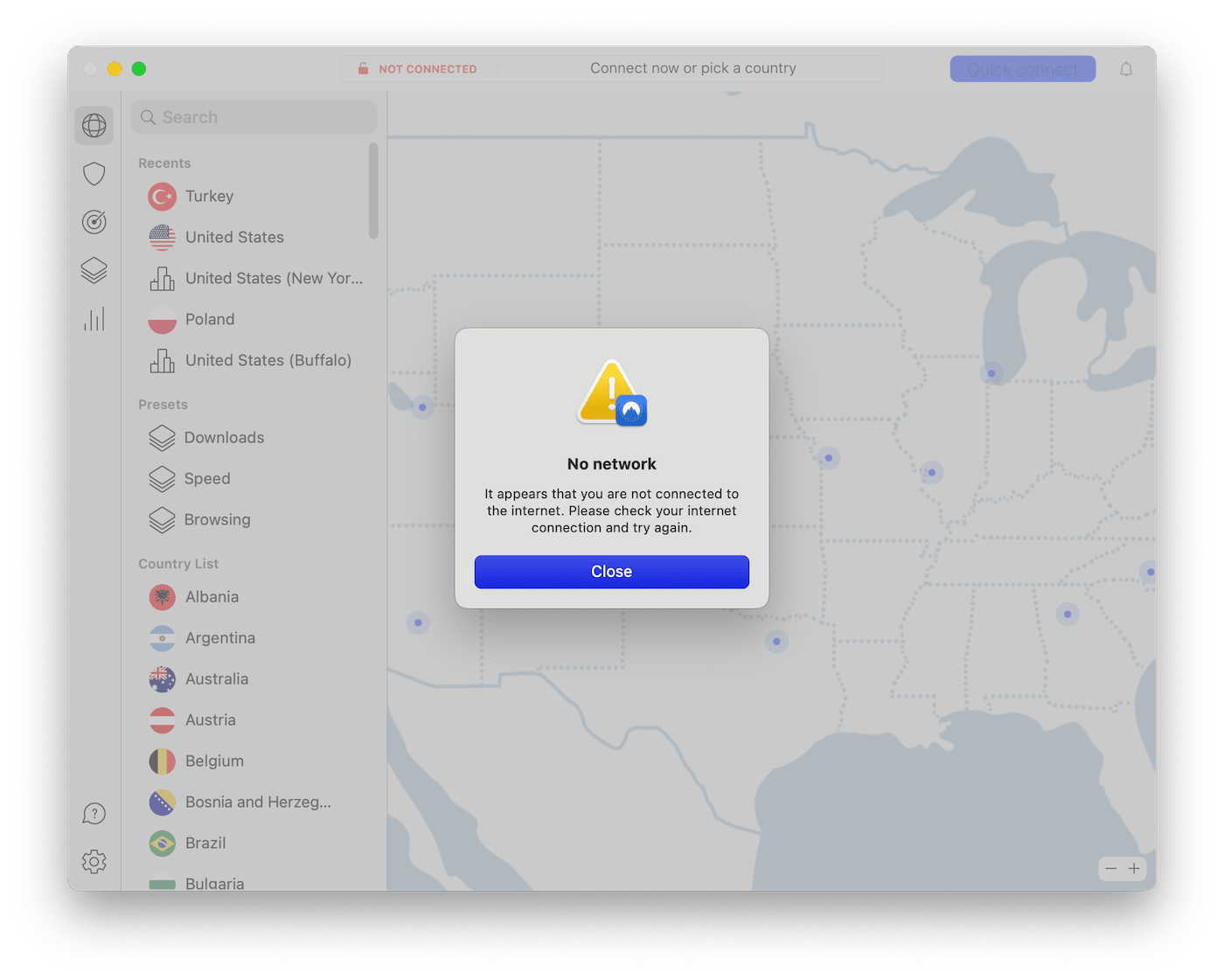
NordVPN not connecting due to network issues.
If you have a weak connection to your WiFi network or mobile data signal, your VPN may struggle to connect to a server.
Whether it’s an issue with your broadband connection, WiFi network, or the router you’re using, you’ll need to fix your internet connection for your VPN to connect properly.
2. The VPN Server is Congested or Undergoing Maintenance
If lots of other users are trying to connect to the same VPN server, the server can get overwhelmed. This is known as server congestion, and it can result in painfully slow speeds and even connection issues.
Server congestion is most common on free VPN services, which typically have a large number of users and a small number of available servers.
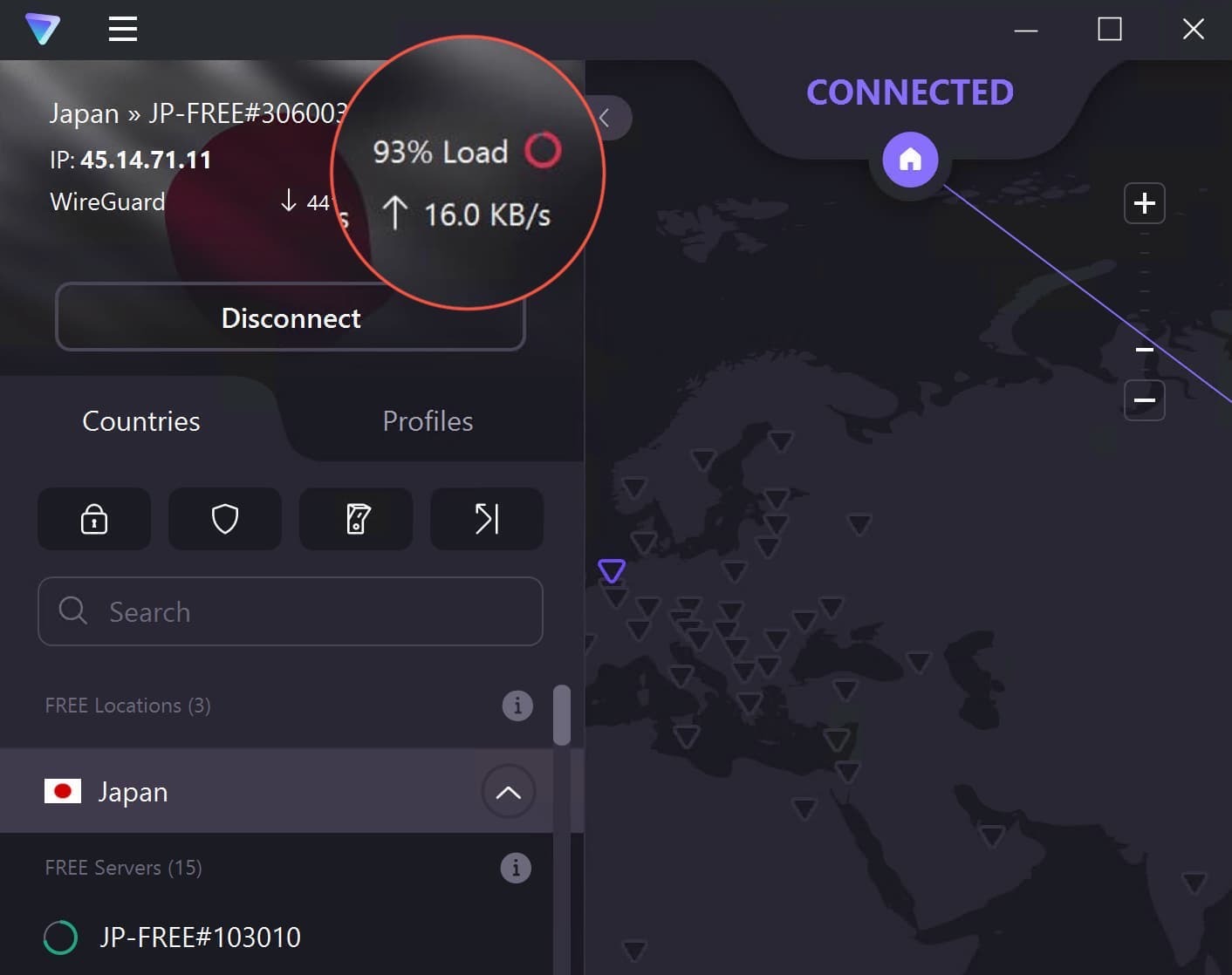
Server congestion using Proton VPN Free.
You might experience similar issues if the server you’ve chosen is undergoing maintenance, or if you’ve reached your VPN’s simultaneous connection limit. In both cases, the VPN application will simply fail to connect altogether.
3. Your Firewall or Antivirus Is Blocking Your VPN
Firewalls work by monitoring incoming and outgoing network traffic, and they can sometimes mistake VPN connections for malicious activity. This can prevent your VPN from connecting.
Network firewalls can be set to blacklist specific IP ranges, to prevent connections to a single IP address, to block specific ports, or even to block all encrypted traffic.
If a VPN service’s traffic is not recognized or is deemed potentially harmful, the firewall may block this traffic. This can happen if the VPN uses unusual ports or protocols that the firewall is not configured to allow.
If you have a firewall enabled on your computer or router, try temporarily disabling it to see if this resolves the issue. If it does, you may need to add an exception for your VPN in the firewall settings. We’ll explain how to do it later on in this guide.
4. Your ISP or the WiFi Network is Blocking VPN Traffic
Public, school, or corporate WiFi networks can sometimes block VPN connections using security software. These networks may have policies in place to restrict VPN usage and prevent any unwanted network activity.
If you are unable to connect to your VPN while using a school, public, or otherwise restricted network, try switching to a different WiFi network or use mobile data if you can.
If you’re at work and need to access your company’s internal network using a VPN, contact your IT department for assistance configuring your device and VPN connection.
In highly-censored countries like China, it’s also possible that your Internet Service Provider (ISP) will attempt to identify and block VPN traffic altogether.
In that case, you’ll need a VPN with obfuscation technology, which disguises your VPN traffic as “normal” traffic.
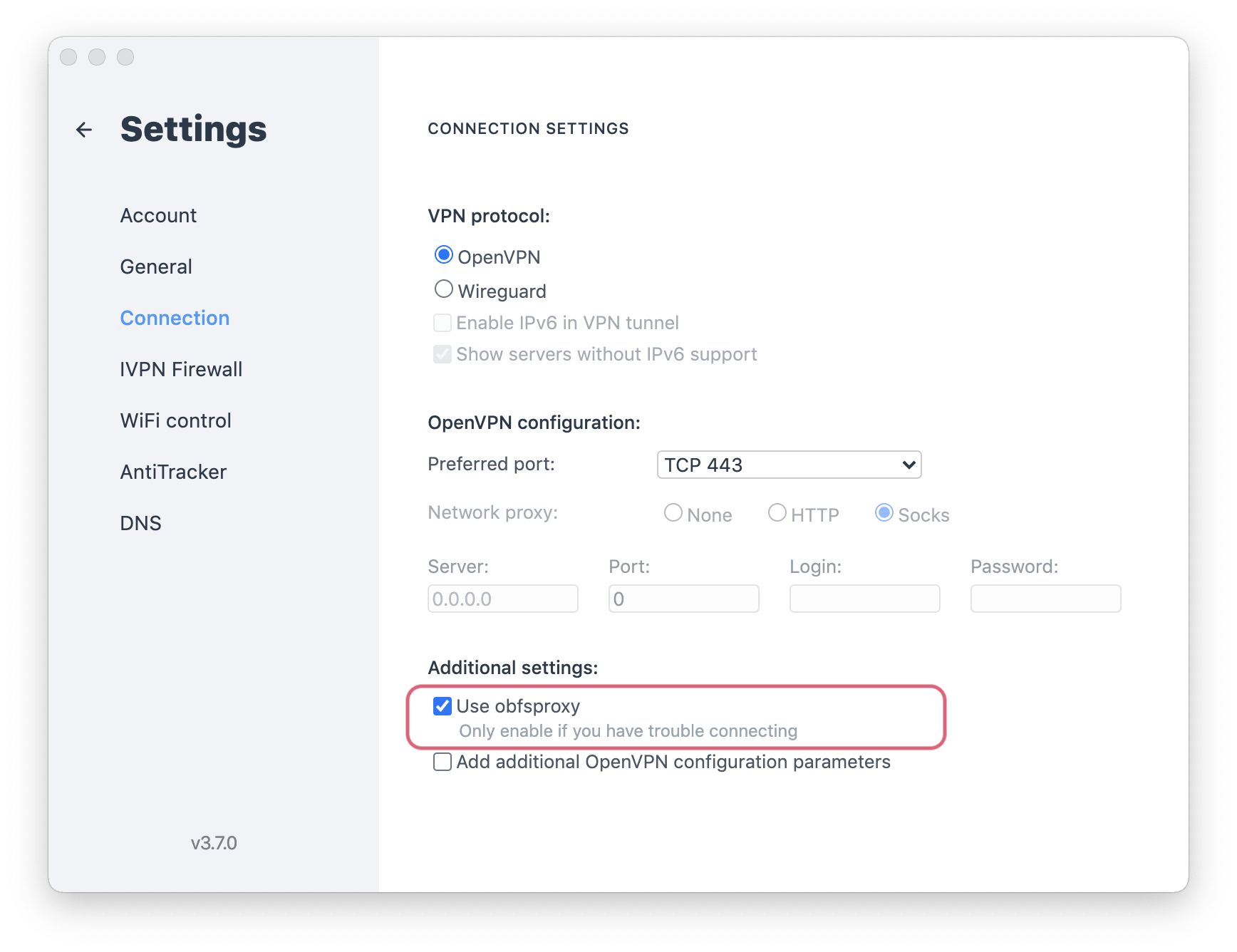
Some VPN services offer obfuscation features to help you connect in highly-censored countries.
.
5. The VPN Software Is Outdated or Too Slow
Making sure your software is up to date is crucial for maintaining a stable VPN connection. Outdated software may not be compatible with your device or the latest security patches, resulting in VPN connection failures.
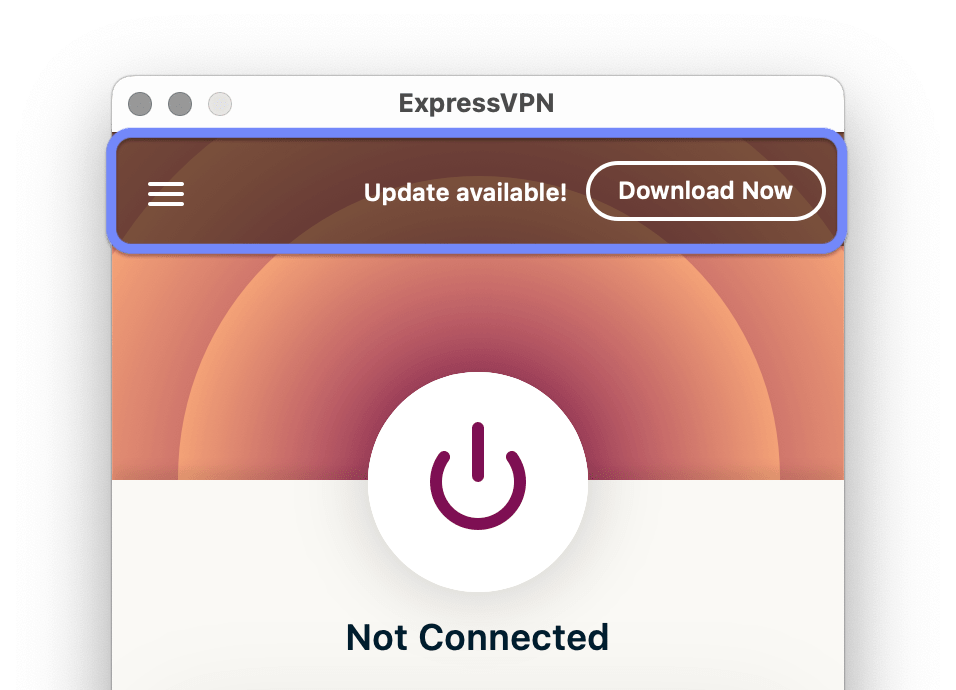
Most VPN services will notify you when the software needs updating.
Slow or poor quality VPNs can also suffer from connection issues. Much like server congestion, this is most commonly an issue with free VPNs that have poor network infrastructure or bandwidth restrictions.
If the VPN server takes too long to respond to your device’s request, the VPN tunnel will simply fail to form.
6. VPN Ports Are Blocked
VPNs use specific ports to establish a connection. Common ports used by VPN protocols include TCP 1723 for PPTP, UDP 500 for IPSec/IKEv2, and UDP 1194 for OpenVPN. These ports need to be open and available for the VPN service to operate effectively.
If these ports are blocked by your ISP, firewall, or router — or they’re not properly configured — it can prevent the VPN from establishing a successful connection.
In some network setups, specific ports need to be forwarded to allow VPN traffic to pass through effectively. If this isn’t set up properly, the VPN client and server might not be able to communicate.
Not all VPNs allow you to change the port your device uses to connect to the internet, but Private Internet Access and IPVanish are both top-tier VPNs that do.
If your router is blocking standard VPN ports, you may need to configure which ports are open manually. This can usually be done through your router’s settings page.
While most VPN services are packaged in apps that handle all the necessary configuration for you, it’s still possible for settings to be misconfigured or for clients to have old settings saved. Most of these issues can be fixed by resetting or reinstalling the app.
If you are connecting to a VPN manually without using an app, ensure you have entered the correct configuration details provided by your VPN provider.