Here’s a summary of the results:
| Testing Category |
Winner |
| Speed |
Custom DNS |
| Bypassing Geo-Restrictions |
VPN |
| Privacy & Security |
VPN |
| Price |
Custom DNS & Smart DNS |
| Device Compatibility |
Custom DNS & Smart DNS |
| Torrenting |
VPN |
| Bypassing Censorship |
VPN |
In short, the best way to protect your privacy and unblock streaming content is to use a VPN service. If you need to bypass geo-restrictions on a device that does not support VPNs, use Smart DNS, which is often cheaper too.
Speed
Custom DNS doesn’t encrypt traffic or route it through a proxy server, meaning it’s usually faster than Smart DNS or VPN services.
In some cases, using a custom DNS server actually meant websites loaded more quickly because we used DNS resolvers that were faster than our ISP’s.
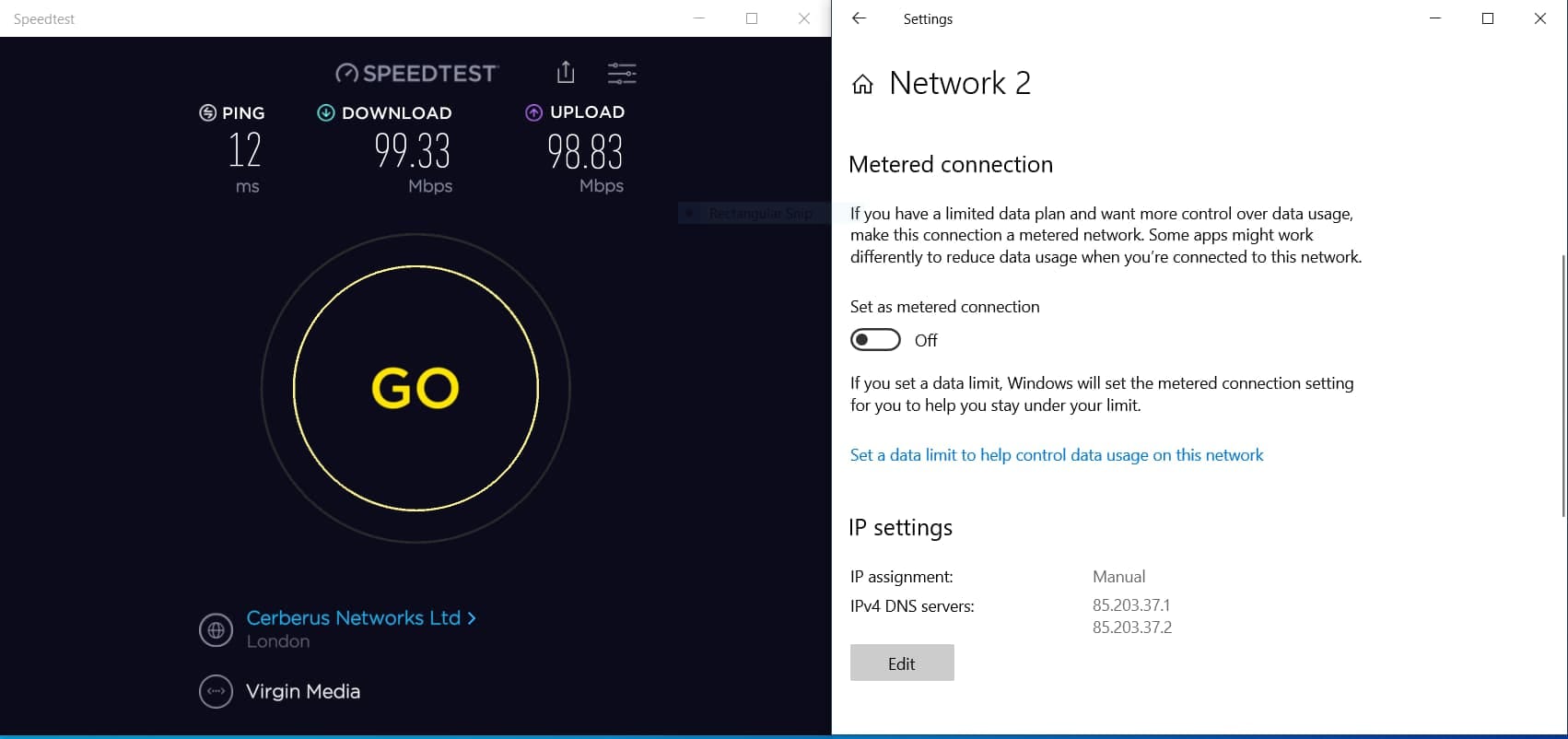
Our tests show custom DNS didn’t negatively impact our download speeds.
In contrast, VPN services encrypt your data and reroute it through a remote server, which can slow down your connection. Though the fastest VPN services minimize this, speed loss can reach 30% or more depending on your VPN provider and the physical distance between you and the VPN server.
Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
Custom DNS will not unblock streaming services, but VPN services and Smart DNS work well. VPNs win in this category, though, as we’ve found that many Smart DNS tools don’t offer the option to manually choose your location.
For instance, the Smart DNS features provided by NordVPN and Surfshark are limited to accessing US streaming services. In contrast, their VPN apps provide access to streaming content from over 100 countries.
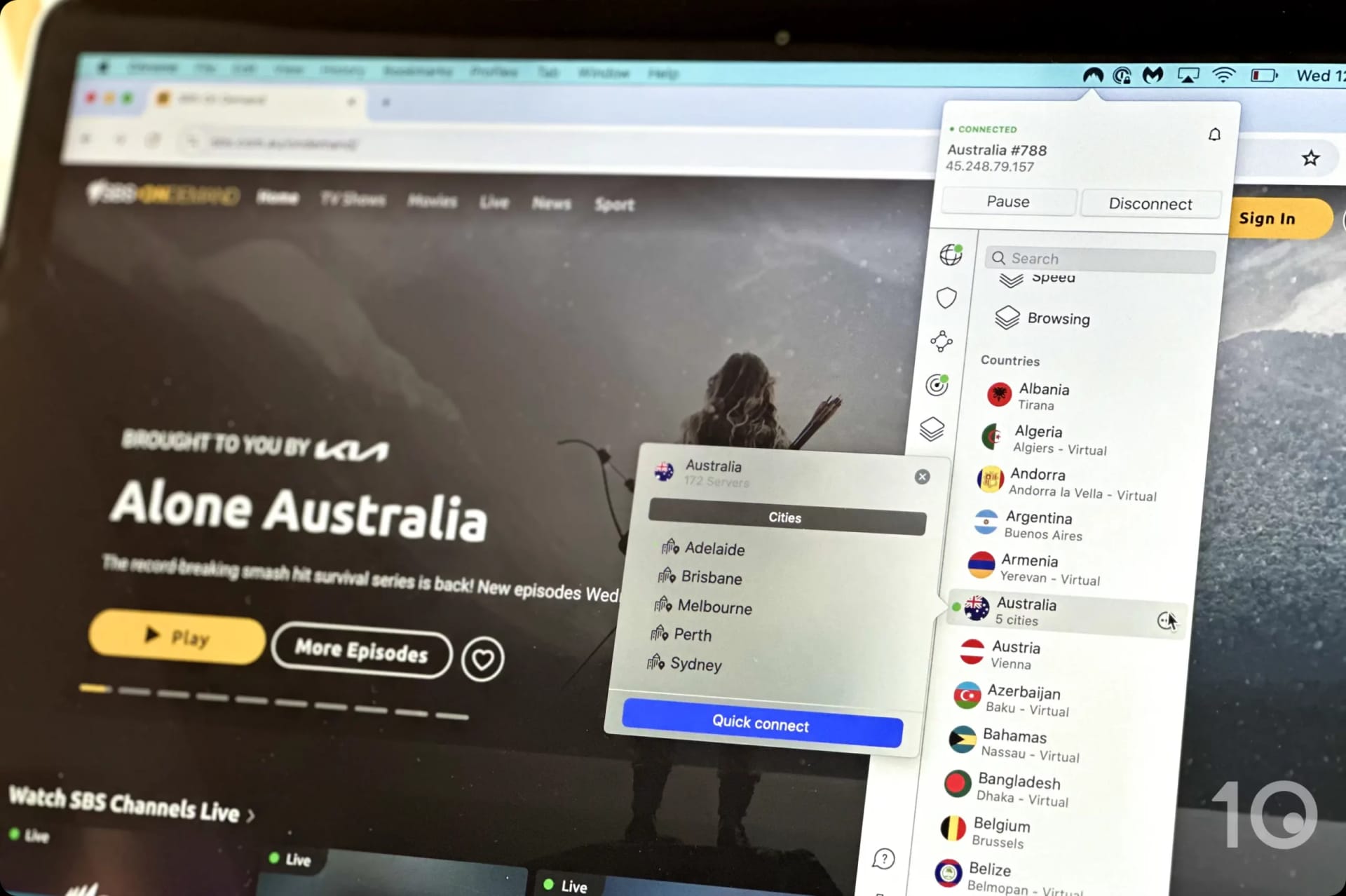
NordVPN’s VPN apps unblock streaming services that its Smart DNS service do not.
That said, we have previously seen Smart DNS sometimes be more reliable at bypassing region restrictions than VPNs on specific platforms. For instance, during the 2021 Netflix VPN ban, ExpressVPN’s MediaStreamer Smart DNS tool maintained access to US Netflix, even though the VPN stopped working.
We recommend choosing a VPN that also offers Smart DNS functionality so that you’re always able to access popular geo-blocked streaming services.
Privacy and Security
Some custom DNS solutions can improve your online security. For example, Google Public DNS benefits from mitigations against DNS cache poisoning attacks, which your ISP might not have in place.
Smart DNS will reroute your DNS requests, but it will not hide your IP address or encrypt your data. Your ISP can see what you are doing online, and can throttle your streaming connection.
Using a VPN is by far the best option for improving your privacy and security. The VPN software will hide your IP address and encrypt your data using robust ciphers like AES-256, which means your ISP cannot monitor your activity.
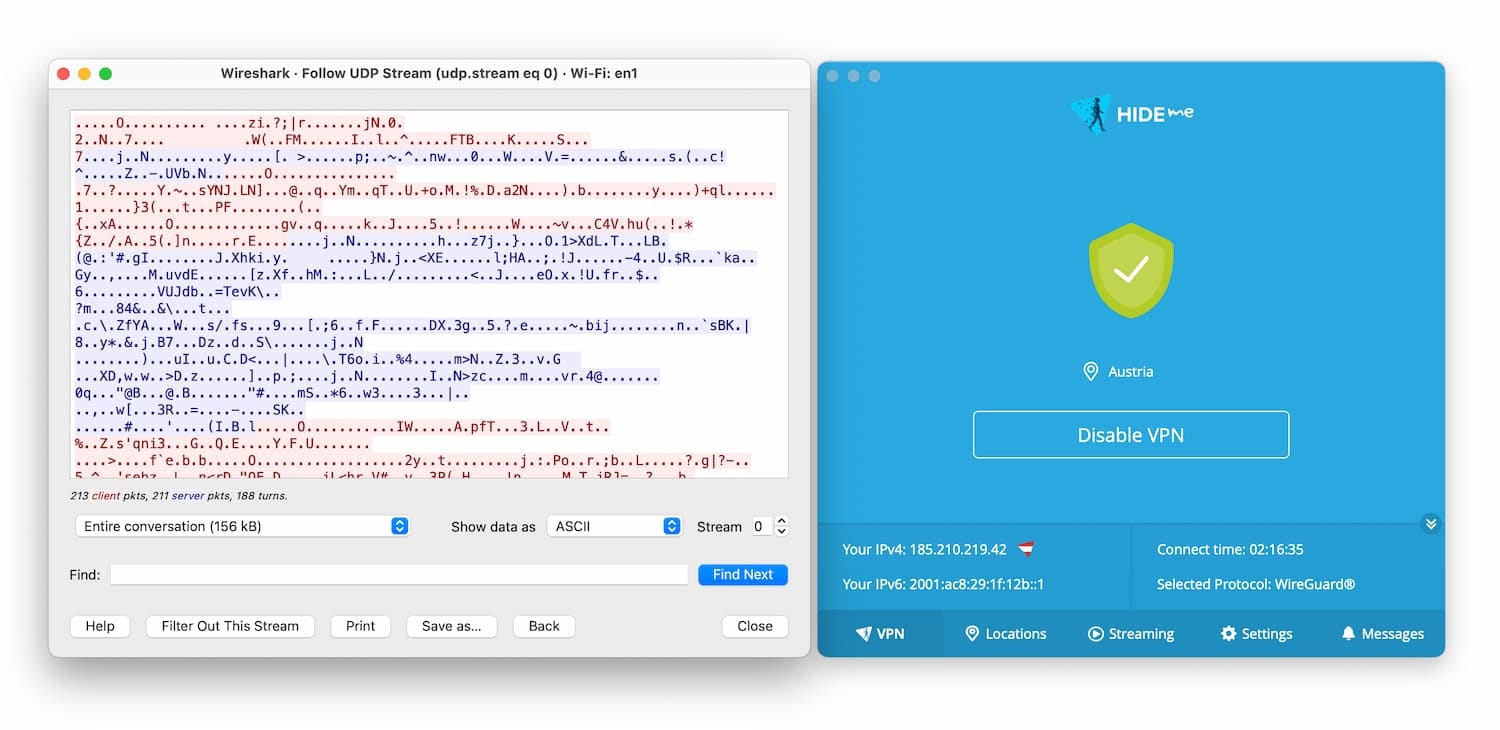
A VPN, like Hide.me, encrypts your browsing data, making it indecipherable.
Price
Winner: Custom DNS & Smart DNS
You’ll have to pay for a reliable Smart DNS or VPN. It’s expensive to maintain the infrastructure required for those services, so free alternatives are likely to be unreliable and may include bandwidth restrictions.
Standalone Smart DNS services are often cheaper than premium VPNs. However, most VPN services usually offer a trial period or a money-back guarantee, which means you can test them before you commit.
Public DNS services are available for free from companies such as Google and Cloudflare.
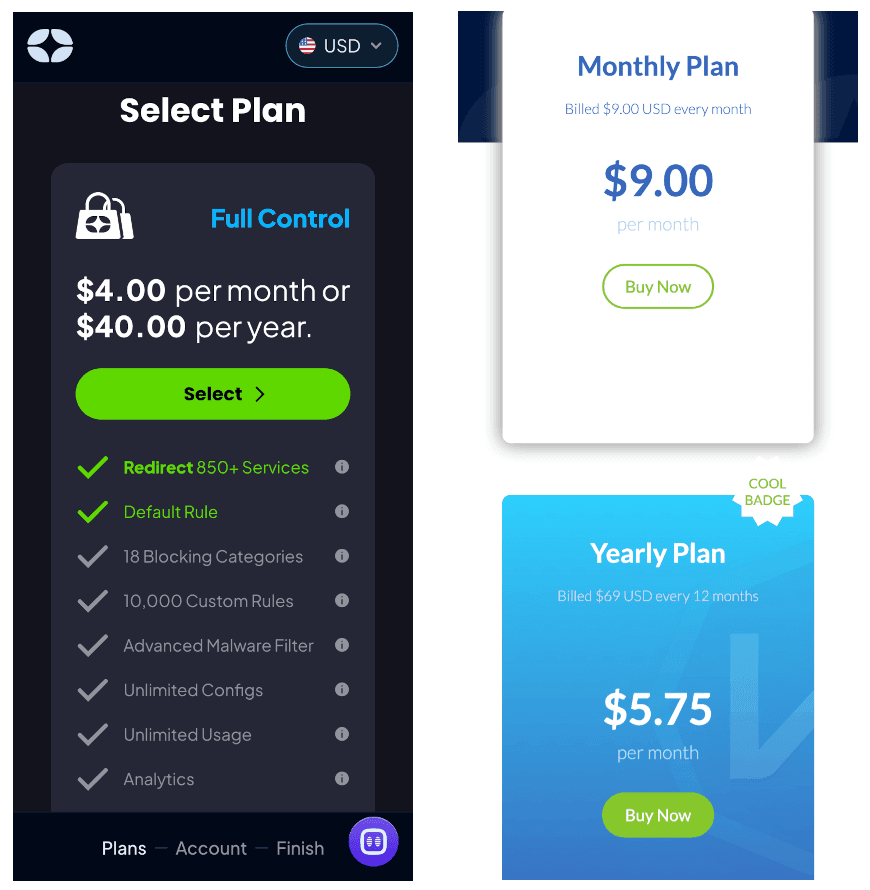
Windscribe’s Smart DNS service (left) is almost half the price of its VPN (right).
Device Compatibility
Winner: Custom DNS & Smart DNS
Custom DNS and Smart DNS work virtually everywhere. Any device that connects to the internet needs to access a DNS server. If you can change your device’s DNS settings, you can use custom DNS or Smart DNS.
This makes Smart DNS a great choice for unblocking region-restricted content on devices such as Smart TVs, PS5, or Xbox.
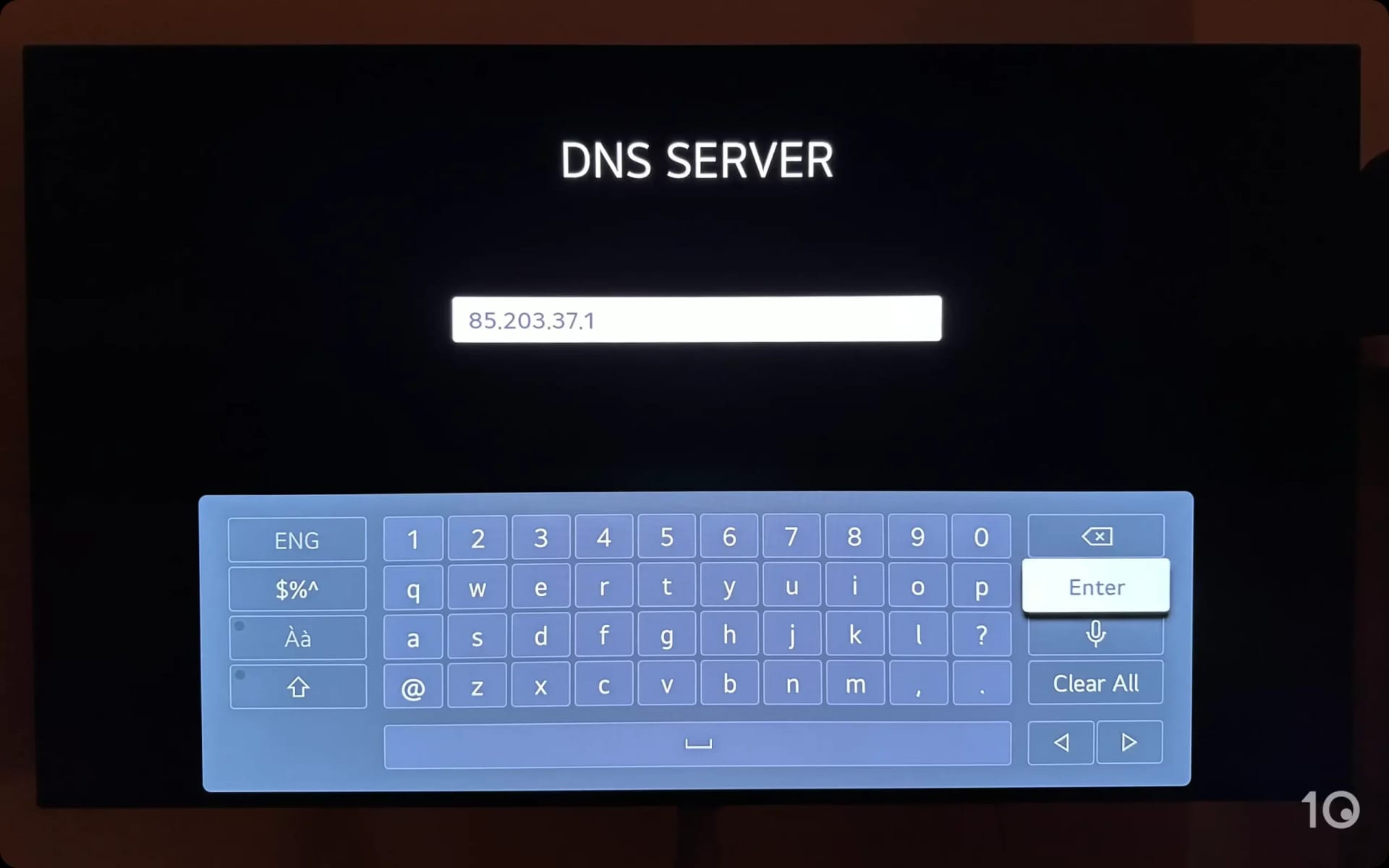
Smart DNS can be configured on devices that don’t support VPN apps, like LG TVs.
Most VPNs provide native applications for Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android. However, you can’t install them on devices like Smart TVs and games consoles.
There are some exceptions to this rule, most notably Roku devices. As these devices don’t allow you to manually change DNS settings, Smart DNS tools are useless.
Instead you’ll have to use one of our recommended VPNs for Roku to unblock streaming content.
You can install a VPN on your router to protect every device on your home network, but this is not a simple process.
Torrenting
Torrenting without a VPN can be dangerous. Without protection, you risk revealing your activity and identity to your ISP, copyright trolls, and other torrenters in the swarm.
Smart DNS and Custom DNS do not hide your IP address, which means they will not keep you safe while torrenting.
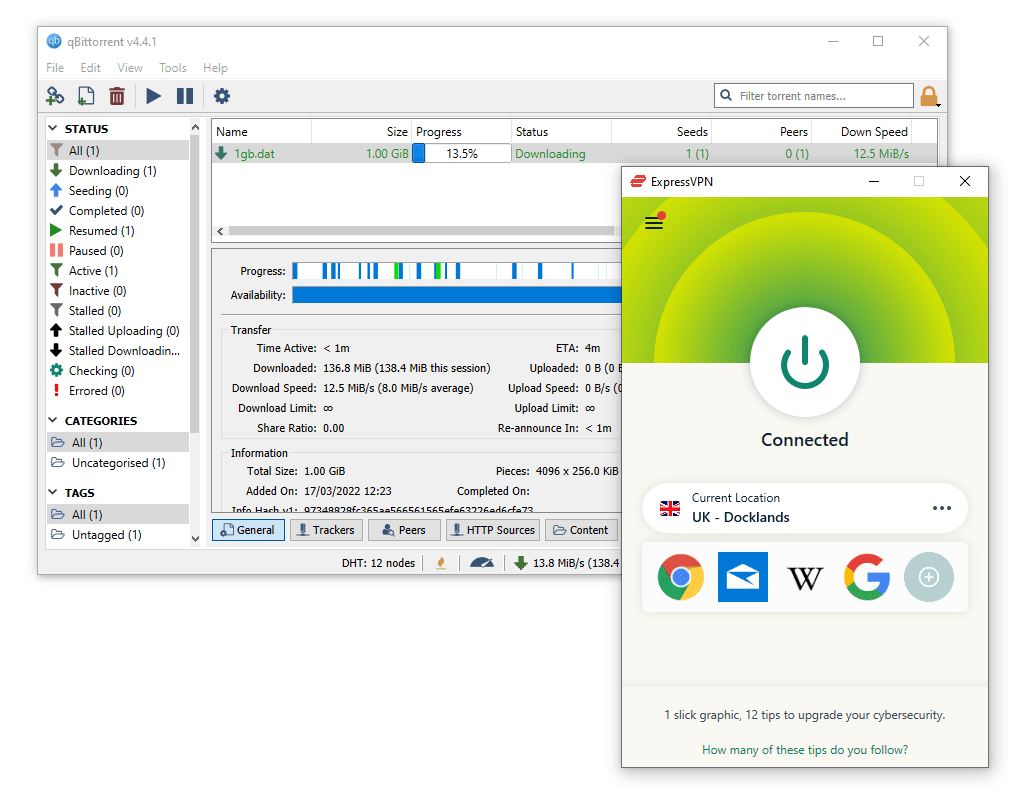
ExpressVPN is fully compatible with BitTorrent clients.
If you torrent using a VPN, the IP address that other users see will be associated with the VPN server you are connecting to, which means it cannot be used to identify you.
Bypassing Censorship
Custom DNS and Smart DNS can help to evade some forms of censorship when imposed at the DNS level.
By changing your DNS servers, it’s possible to evade your ISP’s DNS system and bypass any DNS-based content filtering. It’s also possible to bypass parental control solutions that use DNS queries to block prohibited content.
However, a VPN is the best way to safely unblock websites in highly-censored countries. A VPN will hide your IP address and encrypt your data where Smart DNS does not.
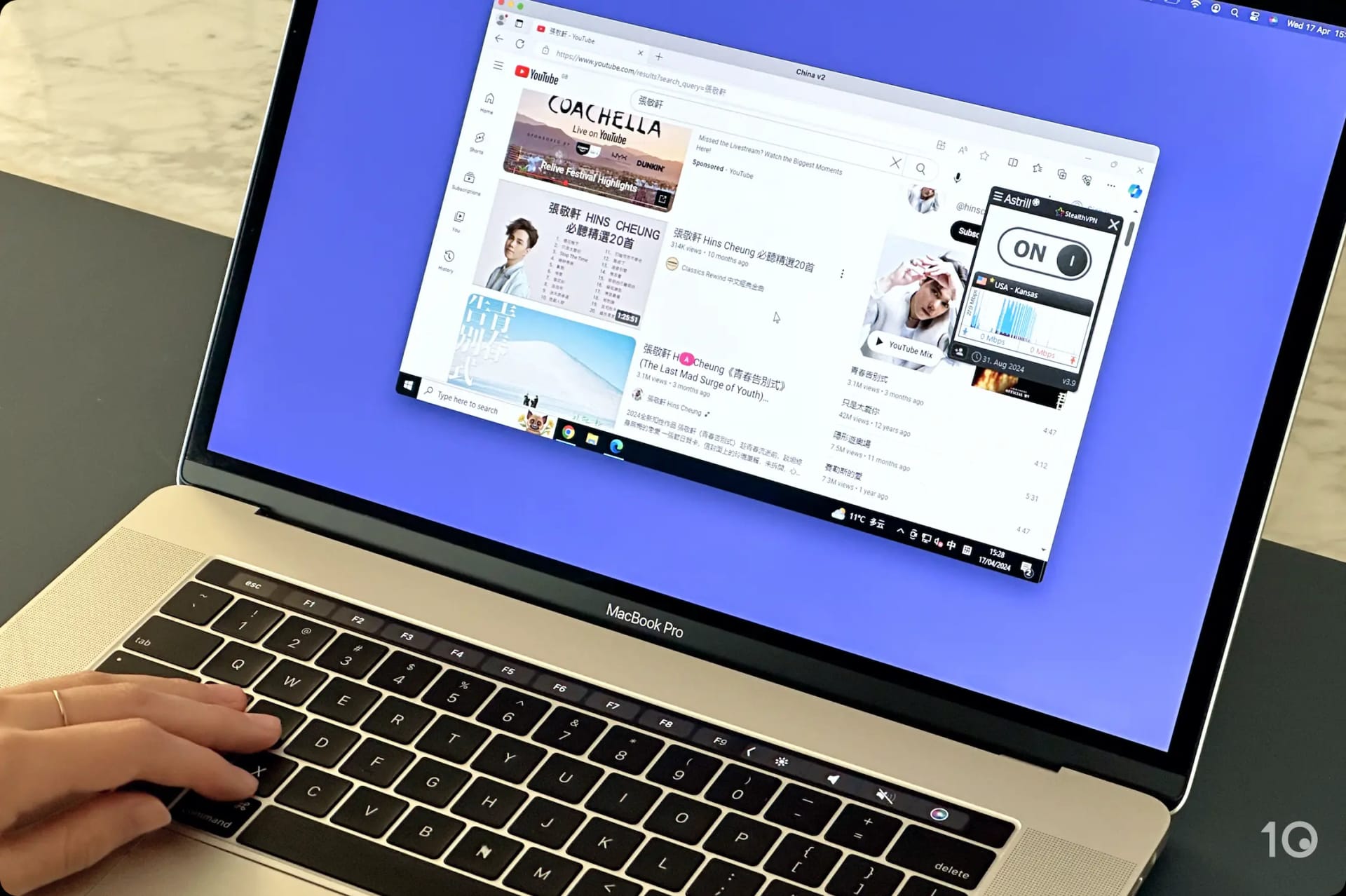
We used Astrill VPN to unblock YouTube in China.
Top-rated VPNs also include obfuscation technology, which disguises VPN traffic as normal HTTPS traffic to help it bypass national firewalls.